Long-Term Dietary Taurine Lowers Plasma Levels of Cholesterol and Bile Acids
- PMID: 35163722
- PMCID: PMC8836270
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031793
Long-Term Dietary Taurine Lowers Plasma Levels of Cholesterol and Bile Acids
Abstract
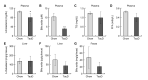
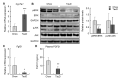
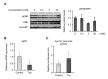
Cholesterol is an essential lipid in vertebrates, but excess blood cholesterol promotes atherosclerosis. In the liver, cholesterol is metabolized to bile acids by cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily a, polypeptide 1 (CYP7A1), the transcription of which is negatively regulated by the ERK pathway. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), a hepatokine, induces ERK phosphorylation and suppresses Cyp7a1 transcription. Taurine, a sulfur-containing amino acid, reportedly promotes cholesterol metabolism and lowers blood and hepatic cholesterol levels. However, the influence of long-term feeding of taurine on cholesterol levels and metabolism remains unclear. Here, to evaluate the more chronic effects of taurine on cholesterol levels, we analyzed mice fed a taurine-rich diet for 14-16 weeks. Long-term feeding of taurine lowered plasma cholesterol and bile acids without significantly changing other metabolic parameters, but hardly affected these levels in the liver. Moreover, taurine upregulated Cyp7a1 levels, while downregulated phosphorylated ERK and Fgf21 levels in the liver. Likewise, taurine-treated Hepa1-6 cells, a mouse hepatocyte line, exhibited downregulated Fgf21 levels and upregulated promoter activity of Cyp7a1. These results indicate that taurine promotes cholesterol metabolism by suppressing the FGF21/ERK pathway followed by upregulating Cyp7a1 expression. Collectively, this study shows that long-term feeding of taurine lowers both plasma cholesterol and bile acids, reinforcing that taurine effectively prevents hypercholesterolemia.
Keywords: CYP7A1; ERK; FGF21; bile acid; cholesterol; taurine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Response in a Preclinical Alcohol Model of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 23;22(15):7898. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157898. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360670 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine ameliorates cholesterol metabolism by stimulating bile acid production in high-cholesterol-fed rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Mar;43(3):372-8. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12534. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26710098
-
Comparative regulation of major enzymes in the bile acid biosynthesis pathway by cholesterol, cholate and taurine in mice and rats.Life Sci. 2005 Jul 1;77(7):746-57. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.11.036. Epub 2005 Mar 19. Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15936349
-
The effect of taurine on cholesterol metabolism.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012 May;56(5):681-90. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201100799. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012. PMID: 22648615 Review.
-
Regulation of cholesterol-7alpha-hydroxylase: BAREly missing a SHP.J Lipid Res. 2002 Apr;43(4):533-43. J Lipid Res. 2002. PMID: 11907135 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct Molecular Action of Taurine on Hepatic Gene Expression Associated with the Amelioration of Hypercholesterolemia in Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 14;13(8):990. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080990. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199235 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Role of Taurine in Aging and Cardiovascular Health: An Updated Overview.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 30;15(19):4236. doi: 10.3390/nu15194236. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do Sex and Gender Interact with the Biological Actions of Taurine? A Critical Rereading of the Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 21;26(16):8097. doi: 10.3390/ijms26168097. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile Acids in Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;12(11):2746. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112746. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic consequences of altered kidney glucose reabsorption under normoglycemic conditions.Mol Metab. 2025 Aug;98:102192. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102192. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Mol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40550327 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

