Understanding Molecular Mechanisms and Identifying Key Processes in Chronic Radiation Cystitis
- PMID: 35163758
- PMCID: PMC8836784
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031836
Understanding Molecular Mechanisms and Identifying Key Processes in Chronic Radiation Cystitis
Abstract
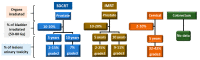
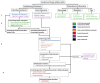
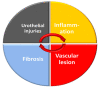
Chronic radiation cystitis (CRC) is a consequence of pelvic radiotherapy and affects 5-10% of patients. The pathology of CRC is without curative treatment and is characterized by incontinence, pelvic pain and hematuria, which severely degrades patients' quality of life. Current management strategies rely primarily on symptomatic measures and have certain limitations. Thanks to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of radiation cystitis, studies targeting key manifestations such as inflammation, neovascularization and cell atrophy have emerged and are promising avenues for future treatment. However, the mechanisms of CRC are still better described in animal models than in human models. Preclinical studies conducted to elucidate the pathophysiology of CRC use distinct models and are most often limited to specific processes, such as fibrosis, vascular damage and inflammation. This review presents a synthesis of experimental studies aimed at improving our understanding of the molecular mechanisms at play and identifying key processes in CRC.
Keywords: cancer; chronic radiation cystitis; fibrosis; inflammation; molecular mechanism; radiotherapy; vascular lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
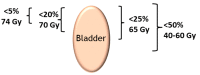

Similar articles
-
Prostate cancer survivors with symptoms of radiation cystitis have elevated fibrotic and vascular proteins in urine.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 29;15(10):e0241388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241388. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33119677 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Inflammation and Radiation-Induced Cystitis: Molecular Background and Therapeutic Perspectives.Cells. 2020 Dec 24;10(1):21. doi: 10.3390/cells10010021. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33374374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Understanding and Managing Radiation Cystitis: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Urol Rep. 2024 Sep 17;26(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s11934-024-01238-0. Curr Urol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39287708 Review.
-
Radiation cystitis modeling: A comparative study of bladder fibrosis radio-sensitivity in C57BL/6, C3H, and BALB/c mice.Physiol Rep. 2020 Feb;8(4):e14377. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14377. Physiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32109348 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Molecular Mechanisms in Radiation Cystitis: Insights from RNA Sequencing.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 23;25(5):2632. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052632. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473879 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Botulinum Toxin A Injections on Patients with Radiogenic Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;17(4):200. doi: 10.3390/toxins17040200. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278698 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Bacille Calmette-Guérin for Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer After Prostate Radiotherapy.Bladder Cancer. 2024 Mar 12;10(1):35-45. doi: 10.3233/BLC-230073. eCollection 2024. Bladder Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38993532 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced cystitis treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy (RICH-ART): long-term follow-up of a randomised controlled, phase 2-3 trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Apr 19;83:103214. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103214. eCollection 2025 May. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40291346 Free PMC article.
-
Maintaining Serum Hemoglobin Levels Within the Physiological Range Prevented Bladder Tamponade Recurrence Due to Radiation-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis: A Case Report.Res Rep Urol. 2023 Aug 21;15:395-401. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S420329. eCollection 2023. Res Rep Urol. 2023. PMID: 37638329 Free PMC article.
-
A Polygenic Risk Score for Late Bladder Toxicity Following Radiotherapy for Non-Metastatic Prostate Cancer.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2025 May 2;34(5):795-804. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-24-1228. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2025. PMID: 40029246
References
-
- The Global Cancer Observatory: International Agency for Research on Cancer: World Health Organization 2020 (Globocan) Number of New Cases in 2020 bs, All Ages and Number of Deaths in 2020, Both Sexes, All Ages. [(accessed on 25 December 2021)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/900-world-fact-she....
-
- INCA Institut National du Cancer: Les Cancers en France en 2018—L’essentiel des Faits et Chiffres (éDition 2019). France: Institut National du Cancer; Février 2019. [(accessed on 25 December 2021)]. 28p. Available online: https://www.e-cancer.fr/Expertises-et-publications/Catalogue-des-publica....
-
- Cesaro S., Brugiolo A., Faraci M., Uderzo C., Rondelli R., Favre C., Zecca M., Garetto G., Dini G., Pillon M., et al. Incidence and treatment of hemorrhagic cystitis in children given hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A survey from the Italian association of pediatric hematology oncology-bone marrow transplantation group. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003;32:925–931. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1704252. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

