Metabolic Reprogramming in Response to Alterations of Mitochondrial DNA and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Gastric Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35163779
- PMCID: PMC8836428
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031857
Metabolic Reprogramming in Response to Alterations of Mitochondrial DNA and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
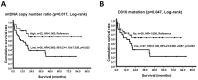
We used gastric cancer cell line AGS and clinical samples to investigate the roles of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) alterations and mitochondrial respiratory dysfunction in gastric adenocarcinoma (GAC). A total of 131 clinical samples, including 17 normal gastric mucosa (N-GM) from overweight patients who had received sleeve gastrectomy and 57 paired non-cancerous gastric mucosae (NC-GM) and GAC from GAC patients who had undergone partial/subtotal/total gastrectomy, were recruited to examine the copy number and D310 sequences of mtDNA. The gastric cancer cell line AGS was used with knockdown (KD) mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) to achieve mitochondrial dysfunction through a decrease of mtDNA copy number. Parental (PT), null-target (NT), and TFAM-KD-(A/B/C) represented the parental, control, and TFAM knocked-down AGS cells, respectively. These cells were used to compare the parameters reflecting mitochondrial biogenesis, glycolysis, and cell migration activity. The median mtDNA copy numbers of 17 N-GM, 57 NC-GM, and 57 GAC were 0.058, 0.055, and 0.045, respectively. The trend of decrease was significant (p = 0.030). In addition, GAC had a lower mean mtDNA copy number of 0.055 as compared with the paired NC-GM of 0.078 (p < 0.001). The mean mtDNA copy number ratio (mtDNA copy number of GAC/mtDNA copy number of paired NC-GM) was 0.891. A total of 35 (61.4%) GAC samples had an mtDNA copy number ratio ≤0.804 (p = 0.017) and 27 (47.4%) harbored a D310 mutation (p = 0.047), and these patients had shorter survival time and poorer prognosis. After effective knockdown of TFAM, TFAM-KD-B/C cells expressed higher levels of hexokinase II (HK-II) and v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1 gene (AKT)-encoded AKT, but lower levels of phosphorylated pyruvate dehydrogenase (p-PDH) than did the NT/PT AGS cells. Except for a higher level of p-PDH, the expression levels of these proteins remained unchanged in TFAM-KD-A, which had a mild knockdown of TFAM. Compared to those of NT, TFAM-KD-C had not only a lower mtDNA copy number (p = 0.050), but also lower oxygen consumption rates (OCR), including basal respiration (OCRBR), ATP-coupled respiration (OCRATP), reserve capacity (OCRRC), and proton leak (OCRPL)(all with p = 0.050). In contrast, TFAM-KD-C expressed a higher extracellular acidification rate (ECAR)/OCRBR ratio (p = 0.050) and a faster wound healing migration at 6, 12, and 18 h, respectively (all with p = 0.050). Beyond a threshold, the decrease in mtDNA copy number, the mtDNA D310 mutation, and mitochondrial dysfunction were involved in the carcinogenesis and progression of GACs. Activation of PDH might be considered as compensation for the mitochondrial dysfunction in response to glucose metabolic reprogramming or to adjust mitochondrial plasticity in GAC.
Keywords: D310 mutation; copy number; gastric adenocarcinoma (GAC); metabolic reprogramming; mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA); mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM); prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

