Theranostic Interpolation of Genomic Instability in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35163783
- PMCID: PMC8836911
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031861
Theranostic Interpolation of Genomic Instability in Breast Cancer
Abstract
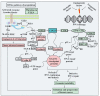
Breast cancer is a diverse disease caused by mutations in multiple genes accompanying epigenetic aberrations of hazardous genes and protein pathways, which distress tumor-suppressor genes and the expression of oncogenes. Alteration in any of the several physiological mechanisms such as cell cycle checkpoints, DNA repair machinery, mitotic checkpoints, and telomere maintenance results in genomic instability. Theranostic has the potential to foretell and estimate therapy response, contributing a valuable opportunity to modify the ongoing treatments and has developed new treatment strategies in a personalized manner. "Omics" technologies play a key role while studying genomic instability in breast cancer, and broadly include various aspects of proteomics, genomics, metabolomics, and tumor grading. Certain computational techniques have been designed to facilitate the early diagnosis of cancer and predict disease-specific therapies, which can produce many effective results. Several diverse tools are used to investigate genomic instability and underlying mechanisms. The current review aimed to explore the genomic landscape, tumor heterogeneity, and possible mechanisms of genomic instability involved in initiating breast cancer. We also discuss the implications of computational biology regarding mutational and pathway analyses, identification of prognostic markers, and the development of strategies for precision medicine. We also review different technologies required for the investigation of genomic instability in breast cancer cells, including recent therapeutic and preventive advances in breast cancer.
Keywords: DNA repair pathways; PARP inhibitor; breast cancer; genomic instability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hertz-Picciotto I., Adams-Campbell L., Devine P., Eaton D., Hammond S., Helzlsouer K., Hiatt R., Hughes-Halbert C., Hunter D., Kramer B. Breast Cancer and the Environment: A Life Course Approach. National Academies Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2012.
-
- Ferlay J.E.M., Lam F., Colombet M., Mery L., Piñeros M., Znaor A., Soerjomataram I., Bray F. Global Cancer Obser-Vatory: Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

