Cytoprotective Activity of Polyamines Is Associated with the Alternative Splicing of RAD51A Pre-mRNA in Normal Human CD4+ T Lymphocytes
- PMID: 35163785
- PMCID: PMC8837172
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031863
Cytoprotective Activity of Polyamines Is Associated with the Alternative Splicing of RAD51A Pre-mRNA in Normal Human CD4+ T Lymphocytes
Abstract
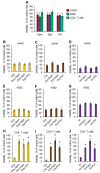
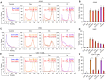
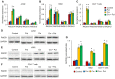
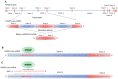
Physiological polyamines are ubiquitous polycations with pleiotropic biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression and cell proliferation as well as modulation of cell signaling. They can also decrease DNA damage and promote cell survival. In the present study, we demonstrated that polyamines have cytoprotective effects on normal human CD4+ T lymphocytes but not on cancer Jurkat or K562 cells. Pretreatment of lymphocytes with polyamines resulted in a significant reduction in cells with DNA damage induced by doxorubicin, cisplatin, or irinotecan, leading to an increase in cell survival and viability. The induction of RAD51A expression was in response to DNA damage in both cancer and normal cells. However, in normal cells, putrescin pretreatment resulted in alternative splicing of RAD51A and the switch of the predominant expression from the splice variant with the deletion of exon 4 to the full-length variant. Induction of RAD51A alternative splicing by splice-switching oligonucleotides resulted in a decrease in DNA damage and cell protection against cisplatin-induced apoptosis. The results of this study suggest that the cytoprotective activity of polyamines is associated with the alternative splicing of RAD51A pre-mRNA in normal human CD4+ T lymphocytes. The difference in the sensitivity of normal and cancer cells to polyamines may become the basis for the use of these compounds to protect normal lymphocytes during lymphoblastic chemotherapy.
Keywords: DNA damage; alternative splicing; apoptosis; cytoprotection; polyamines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zarza X., Van Wijk R., Shabala L., Hunkeler A., Lefebvre M., Rodriguez-Villalón A., Shabala S., Tiburcio A.F., Heilmann I., Munnik T. Lipid kinases PIP5K7 and PIP5K9 are required for polyamine-triggered K(+) efflux in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J. 2020;104:416–432. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14932. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

