miR-132-3p Modulates DUSP9-Dependent p38/JNK Signaling Pathways to Enhance Inflammation in the Amnion Leading to Labor
- PMID: 35163786
- PMCID: PMC8836965
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031864
miR-132-3p Modulates DUSP9-Dependent p38/JNK Signaling Pathways to Enhance Inflammation in the Amnion Leading to Labor
Abstract
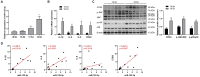
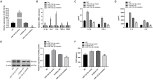
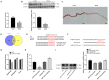
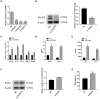
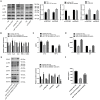
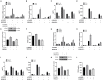
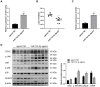
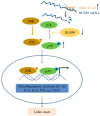
Labor is a process of inflammation and hormonal changes involving both fetal and maternal compartments. MicroRNA-132-3p (miR-132-3p) has been reported to be involved in the development of inflammation-related diseases. However, little is known about its potential role in labor onset. This study aimed to explore the mechanism of miR-132-3p in amnion for labor initiation. In the mouse amnion membranes, the expression of miR-132-3p was found to increase gradually during late gestation. In human amniotic epithelial cell line (WISH), upregulation of miR-132-3p was found to increase proinflammatory cytokines and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) as well as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), which was suppressed by miR-132-3p inhibitor. Dual-specificity phosphatase 9 (DUSP9) was identified as a novel target gene of miR-132-3p, which could be negatively regulated by miR-132-3p. DUSP9 was present in the mouse amnion epithelial cells, with a decrease in its abundance at 18.5 days post coitum (dpc) relative to 15.5 dpc. Silencing DUSP9 was found to facilitate the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and COX2 as well as PGE2 secretion in WISH cells, which could be attenuated by p38 inhibitor SB203580 or JNK inhibitor SP600125. Additionally, intraperitoneal injection of pregnant mice with miR-132-3p agomir not only caused preterm birth, but also promoted the abundance of COX2 as well as phosphorylated JNK and p38 levels, and decreased DUSP9 level in mouse amnion membranes. Collectively, miR-132-3p might participate in inflammation and PGE2 release via targeting DUSP9-dependent p38 and JNK signaling pathways to cause preterm birth.
Keywords: DUSP9; amnion; inflammation; labor; miR-132-3p; p38/JNK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

