Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) Gene Family in Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) Rootstock under Drought Stress Suggested the Potential Role of these Chaperones in Stress Tolerance
- PMID: 35163839
- PMCID: PMC8836791
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031918
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) Gene Family in Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) Rootstock under Drought Stress Suggested the Potential Role of these Chaperones in Stress Tolerance
Abstract
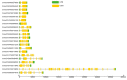
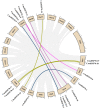
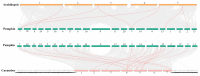
Heat shock protein 70s (HSP70s) are highly conserved proteins that are involved in stress responses. These chaperones play pivotal roles in protein folding, removing the extra amounts of oxidized proteins, preventing protein denaturation, and improving the antioxidant system activities. This conserved family has been characterized in several crops under drought stress conditions. However, there is no study on HSP70s in pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata). Therefore, we performed a comprehensive analysis of this gene family, including phylogenetic relationship, motif and gene structure analysis, gene duplication, collinearity, and promoter analysis. In this research, we found 21 HSP70s that were classified into five groups (from A to E). These genes were mostly localized in the cytoplasm, chloroplast, mitochondria, nucleus, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER). We could observe more similarity in closely linked subfamilies in terms of motifs, the number of introns/exons, and the corresponding cellular compartments. According to the collinearity analysis, gene duplication had occurred as a result of purifying selection. The results showed that the occurrence of gene duplication for all nine gene pairs was due to segmental duplication (SD). Synteny analysis revealed a closer relationship between pumpkin and cucumber than pumpkin and Arabidopsis. Promoter analysis showed the presence of various cis-regulatory elements in the up-stream region of the HSP70 genes, such as hormones and stress-responsive elements, indicating a potential role of this gene family in stress tolerance. We furtherly performed the gene expression analysis of the HSP70s in pumpkin under progressive drought stress. Pumpkin is widely used as a rootstock to improve stress tolerance, as well as fruit quality of cucumber scion. Since stress-responsive mobile molecules translocate through vascular tissue from roots to the whole plant body, we used the xylem of grafted materials to study the expression patterns of the HSP70 (potentially mobile) gene family. The results indicated that all CmoHSP70s had very low expression levels at 4 days after stress (DAS). However, the genes showed different expression patterns by progressing he drought period. For example, the expression of CmoHSP70-4 (in subgroup E) and CmoHSP70-14 (in subgroup C) sharply increased at 6 and 11 DAS, respectively. However, the expression of all genes belonging to subgroup A did not change significantly in response to drought stress. These findings indicated the diverse roles of this gene family under drought stress and provided valuable information for further investigation on the function of this gene family, especially under stressful conditions.
Keywords: chaperones; drought stress; expression pattern; heat shock proteins; phylogeny; pumpkin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of the heat shock transcription factor family in pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata).BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Oct 14;20(1):471. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02683-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33054710 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence analysis of the Hsp70 family in moss and evaluation of their functions in abiotic stress responses.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 20;6:33650. doi: 10.1038/srep33650. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27644410 Free PMC article.
-
Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) HSP20 Gene Family Identification and Expression Under Heat Stress.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 14;12:753953. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.753953. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34721541 Free PMC article.
-
The hsp110 and Grp1 70 stress proteins: newly recognized relatives of the Hsp70s.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2000 Oct;5(4):276-90. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(2000)005<0276:thagsp>2.0.co;2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2000. PMID: 11048651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drought and heat stress-related proteins: an update about their functional relevance in imparting stress tolerance in agricultural crops.Theor Appl Genet. 2019 Jun;132(6):1607-1638. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03331-2. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Theor Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30941464 Review.
Cited by
-
GWAS Reveals a Novel Candidate Gene CmoAP2/ERF in Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) Involved in Resistance to Powdery Mildew.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 10;23(12):6524. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126524. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742978 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of salt and drought stress on the biochemical and molecular functioning of onion cultivars.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Dec 29;51(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08923-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 38157089
-
Peculiar proteome of dark-cultivated Euglena gracilis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25721. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11308-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670614 Free PMC article.
-
Maize heat shock proteins-prospection, validation, categorization and in silico analysis of the different ZmHSP families.Stress Biol. 2023 Sep 6;3(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s44154-023-00104-2. Stress Biol. 2023. PMID: 37981586 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family Under High-Temperature Stress in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 26;26(1):102. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010102. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795969 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

