Enhanced Fear Memories and Altered Brain Glucose Metabolism (18F-FDG-PET) following Subanesthetic Intravenous Ketamine Infusion in Female Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 35163844
- PMCID: PMC8836808
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031922
Enhanced Fear Memories and Altered Brain Glucose Metabolism (18F-FDG-PET) following Subanesthetic Intravenous Ketamine Infusion in Female Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
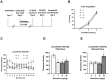
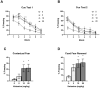
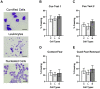
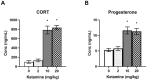
Although women and men are equally likely to receive ketamine following traumatic injury, little is known regarding sex-related differences in the impact of ketamine on traumatic memory. We previously reported that subanesthetic doses of an intravenous (IV) ketamine infusion following fear conditioning impaired fear extinction and altered regional brain glucose metabolism (BGluM) in male rats. Here, we investigated the effects of IV ketamine infusion on fear memory, stress hormone levels, and BGluM in female rats. Adult female Sprague-Dawley rats received a single IV ketamine infusion (0, 2, 10, or 20 mg/kg, over a 2-h period) following auditory fear conditioning (three pairings of tone and footshock). Levels of plasma stress hormones, corticosterone (CORT) and progesterone, were measured after the ketamine infusion. Two days after ketamine infusion, fear memory retrieval, extinction, and renewal were tested over a three-day period. The effects of IV ketamine infusion on BGluM were determined using 18F-fluoro-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG-PET) and computed tomography (CT). The 2 and 10 mg/kg ketamine infusions reduced locomotor activity, while 20 mg/kg infusion produced reduction (first hour) followed by stimulation (second hour) of activity. The 10 and 20 mg/kg ketamine infusions significantly elevated plasma CORT and progesterone levels. All three doses enhanced fear memory retrieval, impaired fear extinction, and enhanced cued fear renewal in female rats. Ketamine infusion produced dose-dependent effects on BGluM in fear- and stress-sensitive brain regions of female rats. The current findings indicate that subanesthetic doses of IV ketamine produce robust effects on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and brain energy utilization that may contribute to enhanced fear memory observed in female rats.
Keywords: brain imaging; fear memory; intravenous ketamine; post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD); sex differences; stress hormone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The opinions and assertions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not reflect the offi-cial policy or position of the Uniformed Services University or the Department of Defense.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of ketamine on fear memory extinction: a review of preclinical literature.Front Neurosci. 2025 Apr 30;19:1546460. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1546460. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40370666 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced fear memories and brain glucose metabolism (18F-FDG-PET) following sub-anesthetic intravenous ketamine infusion in Sprague-Dawley rats.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Nov 30;8(1):263. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0310-8. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30504810 Free PMC article.
-
Association between intravenous ketamine-induced stress hormone levels and long-term fear memory renewal in Sprague-Dawley rats.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jan 27;378:112259. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112259. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31560919
-
Effects of Subanesthetic Intravenous Ketamine Infusion on Corticosterone and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Plasma of Male Sprague-Dawley Rats.AANA J. 2018 Oct;86(5):393-400. AANA J. 2018. PMID: 31584409
-
Effects of Ketamine on Rodent Fear Memory.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 28;21(19):7173. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197173. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32998470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Subanesthetic Intravenous Ketamine Infusion on Stress Hormones and Synaptic Density in Rats with Mild Closed-Head Injury.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 24;13(4):787. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040787. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40299391 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotypic stressors unmask behavioral influences of PMAT deficiency in mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 13:2023.08.30.555632. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.30.555632. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 18;24(22):16494. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216494. PMID: 37693400 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Ketamine differentially affects implicit and explicit memory processes in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Jun;242(6):1245-1258. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06720-8. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 39589435
-
Effects of ketamine on fear memory extinction: a review of preclinical literature.Front Neurosci. 2025 Apr 30;19:1546460. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1546460. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40370666 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotypic Stressors Unmask Behavioral Influences of PMAT Deficiency in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 18;24(22):16494. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216494. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krystal J.H., Karper L.P., Seibyl J.P., Freeman G.K., Delaney R., Bremner J.D., Heninger G.R., Bowers M.B., Jr., Charney D.S. Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in humans: Psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 1994;51:199–214. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950030035004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

