Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Favors Runx2-Mediated Matrix Mineralization in HOS and SaOS2 Cells: An In Vitro and In Silico Approach
- PMID: 35163879
- PMCID: PMC8838199
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030613
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Favors Runx2-Mediated Matrix Mineralization in HOS and SaOS2 Cells: An In Vitro and In Silico Approach
Abstract
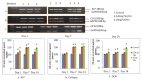
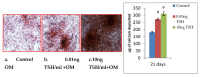
Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease that is both systemic and silent characterized by an unbalanced activity of bone remodeling leading to bone loss. Rising evidences demonstrate that thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) has an important role in the regulation on the metabolism of bone. However, TSH regulation on human osteoblast essential transcriptional factors has not been identified. Current study examined the role of TSH on human osteoblastic Runx2 expression and their functional genes by in vitro and in slico analysis. Human osteoblast like (HOS and SaoS-2) cells were cultured with DMEM and treated with hTSH at the concentration of 0.01 ng/mL and 10 ng/mL. After treatment, osteoblastic Runx2 and IGF-1R beta expression were studied using RT-PCR and western blot analysis. TSH treatment induced osteoblastic essential transcriptional factor, Runx2 in HOS and SaOS2 cells on 48 h duration and elevated the expression of IGF-IR β gene and Protein in SaoS-2 cells. TSH also promotes Runx2 responsive genes such as ALP, Collagen and osteocalcin in SaOS2 cells on day 2 to day 14 of 10 ng/mL of treatment and favors' matrix mineralization matrix in these cells. In addition, TSH facilitated human osteoblastic cells to mineralize their matrix confirmed by day 21 of alizarin red calcium staining. In silico study was performed to check CREB and ELK1 interaction with Runx2. Results of in silico analysis showed that TSH mediated signalling molecules such as CREB and ELK1 showed interaction with Runx2 which involve in osteobalstic gene expression and differentiation. Present findings confirm that TSH promotes Runx2 expression, osteoblastic responsive genes and bone matrix formation.
Keywords: ALP; CREB; ELK1; Runx2; SaOS2; TSH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Mazziotti G., Sorvillo F., Piscopo M., Cioffi M., Pilla P., Biondi B., Iorio S., Giustina A., Amato G., Carella C. Recombinant human TSH modulates in vivo C-telopeptides of type-1 collagen and bone alkaline phosphatase, but not osteoprotegerin production in postmenopausal women monitored for differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005;20:480–486. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.041126. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

