Chondroitin Sulfate Protects the Liver in an Experimental Model of Extra-Hepatic Cholestasis Induced by Common Bile Duct Ligation
- PMID: 35163920
- PMCID: PMC8839946
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030654
Chondroitin Sulfate Protects the Liver in an Experimental Model of Extra-Hepatic Cholestasis Induced by Common Bile Duct Ligation
Abstract
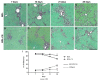
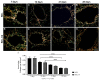
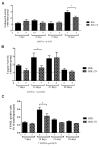
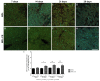
During liver fibrogenesis, there is an imbalance between regeneration and wound healing. The current treatment is the withdrawal of the causing agent; thus, investigation of new and effective treatments is important. Studies have highlighted the action of chondroitin sulfate (CS) in different cells; thus, our aim was to analyze its effect on an experimental model of bile duct ligation (BDL). Adult Wistar rats were subjected to BDL and treated with CS for 7, 14, 21, or 28 days intraperitoneally. We performed histomorphometric analyses on Picrosirius-stained liver sections. Cell death was analyzed according to caspase-3 and cathepsin B activity and using a TUNEL assay. Regeneration was evaluated using PCNA immunohistochemistry. BDL led to increased collagen content with corresponding decreased liver parenchyma. CS treatment reduced total collagen and increased parenchyma content after 21 and 28 days. The treatment also promoted changes in the hepatic collagen type III/I ratio. Furthermore, it was observed that CS treatment reduced caspase-3 activity and the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells after 14 days and cathepsin B activity only after 28 days. The regeneration increased after 14, 21, and 28 days of CS treatment. In conclusion, our study showed a promising hepatoprotective action of CS in fibrogenesis induced by BDL.
Keywords: apoptosis; chondroitin; fibrosis; inflammation; liver; regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Melatonin attenuates oxidative stress, liver damage and hepatocyte apoptosis after bile-duct ligation in rats.Toxicol Ind Health. 2014 Oct;30(9):835-44. doi: 10.1177/0748233712464811. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Toxicol Ind Health. 2014. PMID: 23095487
-
Effects of sphingosylphosphorylcholine against cholestatic oxidative stress and liver damage in the common bile duct ligated rats.J Pediatr Surg. 2009 Apr;44(4):702-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2008.09.016. J Pediatr Surg. 2009. PMID: 19361629
-
Protective effect of Urtica dioica on liver damage induced by biliary obstruction in rats.Toxicol Ind Health. 2013 Oct;29(9):838-45. doi: 10.1177/0748233712445045. Epub 2012 May 14. Toxicol Ind Health. 2013. PMID: 22585933
-
Protective effect of gastrodin on bile duct ligation-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2015 Dec;86:202-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26498411
-
Sildenafil protects against bile duct ligation induced hepatic fibrosis in rats: Potential role for silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1).Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Nov 15;335:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.09.021. Epub 2017 Sep 30. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28974454
Cited by
-
Physicochemical Characteristics and Antidiabetic Properties of the Polysaccharides from Pseudostellaria heterophylla.Molecules. 2022 Jun 9;27(12):3719. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123719. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744844 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-Induced Cytotoxicity and Extracellular Matrix Abnormalities in Hepatocytes Derived From RAD50-Interacting Protein 1-Deficient Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.FASEB J. 2025 Aug 15;39(15):e70909. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500742R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40762441 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Bioglass Into PHBV-Constructed Tissue-Engineered Cartilages to Improve Chondrogenic Properties of Cartilage Progenitor Cells.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 May 23;10:868719. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.868719. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35685093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sepanlou S.G., Safiri S., Bisignano C., Ikuta K.S., Merat S., Saberifiroozi M., Poustchi H., Tsoi D., Colombara D.V., Abdoli A., et al. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020;5:245–266. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu T.Z., Lee K.T., Chern C.L., Cheng J.T., Stern A., Tsai L.Y. Free Radical-Triggered Hepatic Injury of Experimental Obstructive Jaundice of Rats Involves Overproduction of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Enhanced Activation of Nuclear Factor κB. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2001;31:383–390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

