Chondroitin Sulfate Protects the Liver in an Experimental Model of Extra-Hepatic Cholestasis Induced by Common Bile Duct Ligation
- PMID: 35163920
- PMCID: PMC8839946
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030654
Chondroitin Sulfate Protects the Liver in an Experimental Model of Extra-Hepatic Cholestasis Induced by Common Bile Duct Ligation
Abstract
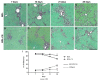
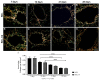
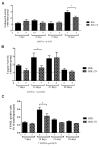
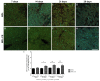
During liver fibrogenesis, there is an imbalance between regeneration and wound healing. The current treatment is the withdrawal of the causing agent; thus, investigation of new and effective treatments is important. Studies have highlighted the action of chondroitin sulfate (CS) in different cells; thus, our aim was to analyze its effect on an experimental model of bile duct ligation (BDL). Adult Wistar rats were subjected to BDL and treated with CS for 7, 14, 21, or 28 days intraperitoneally. We performed histomorphometric analyses on Picrosirius-stained liver sections. Cell death was analyzed according to caspase-3 and cathepsin B activity and using a TUNEL assay. Regeneration was evaluated using PCNA immunohistochemistry. BDL led to increased collagen content with corresponding decreased liver parenchyma. CS treatment reduced total collagen and increased parenchyma content after 21 and 28 days. The treatment also promoted changes in the hepatic collagen type III/I ratio. Furthermore, it was observed that CS treatment reduced caspase-3 activity and the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells after 14 days and cathepsin B activity only after 28 days. The regeneration increased after 14, 21, and 28 days of CS treatment. In conclusion, our study showed a promising hepatoprotective action of CS in fibrogenesis induced by BDL.
Keywords: apoptosis; chondroitin; fibrosis; inflammation; liver; regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Sepanlou S.G., Safiri S., Bisignano C., Ikuta K.S., Merat S., Saberifiroozi M., Poustchi H., Tsoi D., Colombara D.V., Abdoli A., et al. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020;5:245–266. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu T.Z., Lee K.T., Chern C.L., Cheng J.T., Stern A., Tsai L.Y. Free Radical-Triggered Hepatic Injury of Experimental Obstructive Jaundice of Rats Involves Overproduction of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Enhanced Activation of Nuclear Factor κB. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2001;31:383–390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

