Phytochemical Diversity and Antioxidant Potential of Natural Populations of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. throughout the Floristic Regions in Thailand
- PMID: 35163946
- PMCID: PMC8840423
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030681
Phytochemical Diversity and Antioxidant Potential of Natural Populations of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. throughout the Floristic Regions in Thailand
Abstract
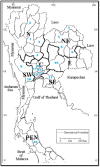
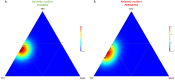
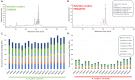
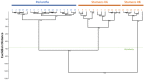
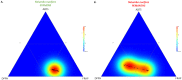
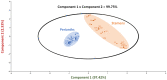
Asian lotus has long been consumed as a food and herbal drug that provides several health benefits. The number of studies on its biological activity is significant, but research at the population level to investigate the variation in phytochemicals and biological activity of each population which is useful for a more efficient phytopharmaceutical application strategy remains needed. This present study provided the frontier results to fill-in this necessary gap to investigating the phytopharmaceutical potential of perianth and stamen, which represent an important part for Asian traditional medicines, from 18 natural populations throughout Thailand by (1) determining their phytochemical profiles, such as total contents of phenolic, flavonoid, and anthocyanin, and (2) determining the antioxidant activity of these natural populations using various antioxidant assays to examine different mechanisms. The result showed that Central is the most abundant floristic region. The stamen was higher in total phenolic and flavonoid contents, whereas perianth was higher in monomeric anthocyanin content. This study provided the first description of the significant correlation between phytochemical contents in perianth compared with stamen extracts, and indicated that flavonoids are the main phytochemical class. This analysis indicated that the stamen is a richer source of flavonoids than perianth, and provided the first report to quantify different flavonoids accumulated in stamen and perianth extracts under their native glycosidic forms at the population level. Various antioxidant assays revealed that major flavonoids from N. nucifera prefer the hydrogen atom transfer mechanism when quenching free radicals. The significant correlations between various phytochemical classes and the different antioxidant tests were noted by Pearson correlation coefficients and emphasized that the antioxidant capability of an extract is generally the result of complex phytochemical combinations as opposed to a single molecule. These current findings offer the alternative starting materials to assess the phytochemical diversity and antioxidant potential of N. nucifera for phytopharmaceutical sectors.
Keywords: Nelumbo nucifera; Nelumbonaceae; antioxidant potential; floristic regions; phytochemical profiles; population level; sacred lotus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dezhi F., Wiersema J.H. Flora of China. Science Press; Beijing, China: Missouri Botanical Garden Press; St. Louis, MO, USA: 2001. Nelumbo nucifera; p. 1.
-
- Chayamarit K., Balslav H., Esser H.J. In: Flora of Thailand. Chayamarit K., Balslav H., editors. The Forest Herbarium, Royal Forest Department; Bangkok, Thailand: 2020. 14/4.
-
- Shen-Miller J., Mudgett M.B., Schopf J.W., Clarke S., Berger R. Exceptional Seed Longevity and Robust Growth: Ancient Sacred Lotus from China. Am. J. Bot. 1995;82:1367–1380. doi: 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1995.tb12673.x. - DOI
-
- Sikarwar R.L.S. Angiosperm diversity assessment of Chitrakootthe legendary place of Vindhyan range. India J. Econ. Taxon. Bot. 2014;38:563–619.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

