Separation and Enrichment of Alkaloids from Coptidis Rhizoma and Euodiae Fructus by Macroporous Resin and Evaluation of the Effect on Bile Reflux Gastritis Rats
- PMID: 35163988
- PMCID: PMC8839576
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030724
Separation and Enrichment of Alkaloids from Coptidis Rhizoma and Euodiae Fructus by Macroporous Resin and Evaluation of the Effect on Bile Reflux Gastritis Rats
Abstract
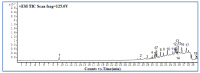
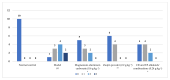
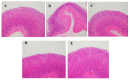
The Zuojin Pill consists of Coptidis Rhizoma (CR) and Euodiae Fructus (EF). It has been a classic prescription for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases in China since ancient times. Alkaloids are considered to be its main pharmacologically active substances. The authors of the present study investigated the feasibility of preparing high purity total alkaloids (TAs) from CR and EF extracts separately and evaluated the effect for the treatment of bile reflux gastritis (BRG). Coptis chinensis Franch. and Evodia rutaecarpa (Juss.) Benth. were used in the study. An optimized method for the enrichment and purification of TAs with macroporous resin was established. Furthermore, qualitative analysis by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization and quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS) was explored to identify the components of purified TAs. Thirty-one compounds, thirty alkaloids and one phenolic compound, were identified or tentatively assigned by comparison with reference standards or literature data. A method of ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detector (UHPLC-DAD) for quantitative analysis was also developed. The contents of nine alkaloids were determined. Moreover, a rat model of BRG was used to investigate the therapeutic effect of the combination of purified TAs from CR and EF. Gastric pathologic examination suggested that the alkaloids' combination could markedly attenuate the pathological changes of gastric mucosa.
Keywords: Coptidis Rhizoma; Euodiae Fructus; UHPLC–DAD; UHPLC–ESI–QTOF-MS; bile reflux gastritis; enrichment and purification; gastric pathology; macroporous resin; rats; total alkaloids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation of the Coptidis Rhizoma and Euodiae Fructus Herbal Pair by Using UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS and UHPLC-DAD.Molecules. 2020 Oct 18;25(20):4782. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204782. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33081031 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of alginate-chitosan microspheres loaded with alkaloids from Coptis chinensis Franch. and Evodia rutaecarpa (Juss.) Benth. (Zuojin Pill) against ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal injury in rats.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Nov 19;9:6151-65. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S96056. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26640368 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of active alkaloids and metabolites in rats after oral administration of Zuojin Pill using UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with bioinformatics and molecular docking analyses.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024 Oct 15;249:116340. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116340. Epub 2024 Jul 4. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024. PMID: 38986349
-
Chromatographic and mass spectrometric technologies for chemical analysis of Euodiae fructus: A review.Phytochem Anal. 2023 Jan;34(1):5-29. doi: 10.1002/pca.3187. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Phytochem Anal. 2023. PMID: 36442477 Review.
-
[Research on Chinese medicine pairs (VI)--Coptidis Rhizoma-Euodiae fructus].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Dec;38(24):4214-9. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24791519 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Euodiae Fructus: a review of botany, application, processing, phytochemistry, quality control, pharmacology, and toxicology.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1509032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1509032. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39944619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive fecal metabolomics and gut microbiota study of the protective mechanism of herbal pair Polygonum hydropiper-Coptis chinensis in rats with stress-induced gastric mucosal damage.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 13;15:1435166. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1435166. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39193339 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics Profiles Reveal the Efficacy of Wuzhuyu Decoction on Patients with Chronic Non-Atrophic Gastritis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Nov 7;17:3269-3280. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S428783. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37954485 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Macroporous Resin Combined Extraction and Purification of Polyphenols from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. and Anti-Tumor Effect In Vitro.Molecules. 2025 Mar 26;30(7):1478. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071478. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286126 Free PMC article.
-
Zhuyu Pill Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Bile Acid Metabolism through the Gut-Liver Axis.ACS Omega. 2023 Aug 2;8(32):29033-29045. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01955. eCollection 2023 Aug 15. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37599938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Editorial Committee of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Chemical Technology Press; Shanghai, China: 2020. p. 802.
-
- Zhang H.M., Wang C.H., Wang Z.T. Simultaneous analysis of protoberberine and indolequinoline alkaloids in Zuojin Pill extract by high-performance liquid chromatography. Acta Chromatogr. 2013;25:589–600. doi: 10.1556/AChrom.25.2013.3.14. - DOI
-
- Wang L.Y., Tang Y.P., Liu X., Ge Y.H., Li W.X. Research on Chinese medicine pairs (VI)--Coptidis Rhizoma-Euodiae fructus. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013;38:4214–4219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

