Phytochemical Characterization, Antioxidant Activity, and Cytotoxicity of Methanolic Leaf Extract of Chlorophytum Comosum (Green Type) (Thunb.) Jacq
- PMID: 35164026
- PMCID: PMC8840168
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030762
Phytochemical Characterization, Antioxidant Activity, and Cytotoxicity of Methanolic Leaf Extract of Chlorophytum Comosum (Green Type) (Thunb.) Jacq
Abstract
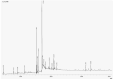
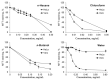
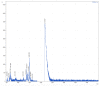
Chlorophytum genus has been extensively studied due to its diverse biological activities. We evaluated the methanolic extract of leaves of Chlorophytum comosum (Green type) (Thunb.) Jacques, the species that is less studied compared to C. borivilianum. The aim was to identify phytoconstituents of the methanolic extract of leaves of C. comosum and biological properties of its different fractions. Water fraction was analyzed with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry. Nineteen compounds belonging to different chemical classes were identified in the methanolic extract of leaves of C. comosum (Green type) (Thunb.) Jacques. In addition to several fatty acids, isoprenoid and steroid compounds were found among the most abundant constituents. One of the identified compounds, 4'-methylphenyl-1C-sulfonyl-β-d-galactoside, was not detected earlier in Chlorophytum extracts. The water fraction was toxic to HeLa cells but not to Vero cells. Our data demonstrate that methanolic extract of leaves of C. comosum can be a valuable source of bioactive constituents. The water fraction of the extract exhibited promising antitumor potential based on a high ratio of HeLa vs. Vero cytotoxicity.
Keywords: Chlorophytum comosum; antioxidant activity; biological active substances; cytotoxicity; herbal medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kaushik N. Saponins of Chlorophytum species. Phytochem. Rev. 2005;4:191–196. doi: 10.1007/s11101-005-2607-5. - DOI
-
- Patil S.M., Chandanshive V.V., Tamboli A.S., Adsul A.A., Yadav S.R., Govindwar S.P. Analysis of genetic variability in endemic medicinal plants of genus Chlorophytum from the Indian subcontinent using amplified fragment length polymorphism marker. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2015;338:838–845. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2015.09.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Munyao J.N., Dong X., Yang J.-X., Mbandi E.M., Wanga V.O., Oulo M.A., Saina J.K., Musili P.M., Hu G.-W. Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Chlorophytum comosum and Chlorophytum gallabatense: Genome Structures, Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis. Plants. 2020;9:296. doi: 10.3390/plants9030296. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deore S.L., Jajoo N.B., Chittam K.P., Deshmukh T.A. Comparative Pharmacognostic, Phytochemical and Biological evaluation between five Chlorophytum species. Pharmacogn. J. 2015;7:317–325. doi: 10.5530/pj.2015.5.12. - DOI
-
- Khare C.P. Indian Medicinal Plants. In: Khare C.P., editor. An Illustrated Dictionary. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2007. p. 68. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

