Yeast GH30 Xylanase from Sugiyamaella lignohabitans Is a Glucuronoxylanase with Auxiliary Xylobiohydrolase Activity
- PMID: 35164030
- PMCID: PMC8840591
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030751
Yeast GH30 Xylanase from Sugiyamaella lignohabitans Is a Glucuronoxylanase with Auxiliary Xylobiohydrolase Activity
Abstract
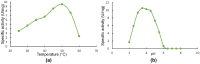
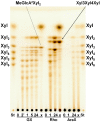
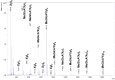
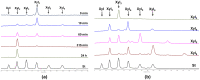
Xylanases are the enzymes that catalyze the breakdown of the main hemicellulose present in plant cell walls. They have attracted attention due to their biotechnological potential for the preparation of industrially interesting products from lignocellulose. While many xylanases have been characterized from bacteria and filamentous fungi, information on yeast xylanases is scarce and no yeast xylanase belonging to glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 30 has been described so far. Here, we cloned, expressed and characterized GH30 xylanase SlXyn30A from the yeast Sugiyamaella lignohabitans. The enzyme is active on glucuronoxylan (8.4 U/mg) and rhodymenan (linear β-1,4-1,3-xylan) (3.1 U/mg) while its activity on arabinoxylan is very low (0.03 U/mg). From glucuronoxylan SlXyn30A releases a series of acidic xylooligosaccharides of general formula MeGlcA2Xyln. These products, which are typical for GH30-specific glucuronoxylanases, are subsequently shortened at the non-reducing end, from which xylobiose moieties are liberated. Xylobiohydrolase activity was also observed during the hydrolysis of various xylooligosaccharides. SlXyn30A thus expands the group of glucuronoxylanases/xylobiohydrolases which has been hitherto represented only by several fungal GH30-7 members.
Keywords: GH30-7 subfamily; Sugiyamaella lignohabitans; glucuronoxylanase; glycoside hydrolase family 30; xylan; xylanase; xylobiohydrolase; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Catalytic Diversity of GH30 Xylanases.Molecules. 2021 Jul 27;26(15):4528. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154528. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361682 Free PMC article.
-
GH30-7 Endoxylanase C from the Filamentous Fungus Talaromyces cellulolyticus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Oct 30;85(22):e01442-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01442-19. Print 2019 Nov 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31492671 Free PMC article.
-
A novel GH30 xylobiohydrolase from Acremonium alcalophilum releasing xylobiose from the non-reducing end.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020 Mar;134:109484. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.109484. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020. PMID: 32044031
-
Xylanases of glycoside hydrolase family 30 - An overview.Biotechnol Adv. 2021 Mar-Apr;47:107704. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107704. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Biotechnol Adv. 2021. PMID: 33548454 Review.
-
Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005 Jan;29(1):3-23. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.06.005. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15652973 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: An update for 2021-2022.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025 May-Jun;44(3):213-453. doi: 10.1002/mas.21873. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025. PMID: 38925550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for targeted hydrolysis and fermentation of glucuronoxylan through CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Mar 16;23(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02361-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 38493086 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and secretomic analyses of Blastobotrys yeasts reveal key xylanases for biomass decomposition.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 1;109(1):175. doi: 10.1007/s00253-025-13556-5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40748385 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptococcus laurentii: a wild yeast for xylanase production from agricultural by-products.Int Microbiol. 2025 Mar;28(3):437-445. doi: 10.1007/s10123-024-00555-1. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Int Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 38970730
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

