Zingiber officinale var. rubrum: Red Ginger's Medicinal Uses
- PMID: 35164040
- PMCID: PMC8840670
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030775
Zingiber officinale var. rubrum: Red Ginger's Medicinal Uses
Abstract
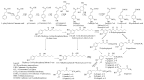
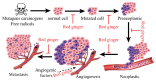
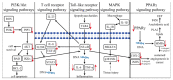
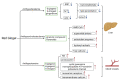
Zingiber officinale var. rubrum (red ginger) is widely used in traditional medicine in Asia. Unlike other gingers, it is not used as a spice in cuisines. To date, a total of 169 chemical constituents have been reported from red ginger. The constituents include vanilloids, monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, flavonoids, amino acids, etc. Red ginger has many therapeutic roles in various diseases, including inflammatory diseases, vomiting, rubella, atherosclerosis, tuberculosis, growth disorders, and cancer. Scientific evidence suggests that red ginger exhibits immunomodulatory, antihypertensive, antihyperlipidemic, antihyperuricemic, antimicrobial, and cytotoxic activities. These biological activities are the underlying causes of red ginger's therapeutic benefits. In addition, there have been few reports on adverse side effects of red ginger. This review aims to provide insights in terms the bioactive constituents and their biosynthesis, biological activities, molecular mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, and qualitative and quantitative analysis of red ginger.
Keywords: Zingiber officinale var. rubrum; analysis; bioactive constituents; biological activities; biosynthesis; molecular mechanisms; pharmacokinetics; red ginger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ginger--an herbal medicinal product with broad anti-inflammatory actions.J Med Food. 2005 Summer;8(2):125-32. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2005.8.125. J Med Food. 2005. PMID: 16117603 Review.
-
Zingiber Officinale Roscoe: The Antiarthritic Potential of a Popular Spice-Preclinical and Clinical Evidence.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 5;16(5):741. doi: 10.3390/nu16050741. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of encapsulant materials on the stability of bioactive compounds of red ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe. var. Rubrum) extract powder during storage.Food Chem. 2020 Dec 15;333:127490. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127490. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32653682
-
Antioxidant and inhibitory effect of red ginger (Zingiber officinale var. Rubra) and white ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) on Fe(2+) induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain in vitro.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2012 Jan;64(1-2):31-6. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2010.06.002. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 20598871
-
Chemical constituents and their bioactivities of "Tongling White Ginger" (Zingiber officinale).J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Nov 9;59(21):11690-5. doi: 10.1021/jf202544w. Epub 2011 Oct 7. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21954969
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Constituents and Antiproliferative Activities of Essential Oils from Four Varieties of Malaysian Zingiber officinale Roscoe against Human Cervical Cancer Cell Line.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 10;11(10):1280. doi: 10.3390/plants11101280. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631703 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of red ginger powder (Zingiber officinale var. rubrum) as a feed additive for starter and finisher broiler chicken to increase immunoglobulin A and immunoglobulin Y expression and to prevent intestinal injury due to Salmonella enteritidis infection.Vet World. 2022 Jun;15(6):1506-1514. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2022.1506-1514. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Vet World. 2022. PMID: 35993070 Free PMC article.
-
Antiplatelet Effects of a Combination of Sappan Wood (Caesalpinia sappan L.) and Red Ginger (Zingiber officinale var. Rubrum) Extracts in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Rat Model.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 Dec 20;2024:5543717. doi: 10.1155/adpp/5543717. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39734397 Free PMC article.
-
Essential oil-derived compounds target core fatigue-related genes: A network pharmacology and molecular Docking approach.PLoS One. 2025 May 28;20(5):e0314125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314125. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40435272 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Zingiber officinale to reduce inflammation markers and the length of stay of patients with community-acquired pneumonia: An open-label clinical trial.Narra J. 2023 Apr;3(1):e142. doi: 10.52225/narra.v3i1.142. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Narra J. 2023. PMID: 38450038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Syafitri D.M., Levita J., Mutakin M., Diantini A. A Review: Is Ginger (Zingiber officinale var. Roscoe) Potential for Future Phytomedicine? Indones. J. Appl. Sci. 2018;8:30. doi: 10.24198/ijas.v8i1.16466. - DOI
-
- Setyawan A.D., Wiryanto W., Suranto S., Bermawie N. Short Communication: Variation in isozymic pattern of germplasm from three ginger (Zingiber officinale) varieties. Nusant. Biosci. 1970;6:113. doi: 10.13057/nusbiosci/n060113. - DOI
-
- Safitri A.R., Evanuarini H., Thohari I. The Potential of Local Ginger as Antioxidant on Full Fat Mayonnaise. J. Ilmu dan Teknol. Has. Ternak. 2019;14:90–98. doi: 10.21776/ub.jitek.2019.014.02.3. - DOI
-
- Sivasothy Y., Chong W.K., Hamid A., Eldeen I.M., Sulaiman S.F., Awang K. Essential oils of Zingiber officinale var. rubrum Theilade and their antibacterial activities. Food Chem. 2011;124:514–517. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.06.062. - DOI
-
- Kusumawati N., Anggarani M.A., Rusijono, Setiarso P., Muslim S. Product standarization of ginger (Zingiber officinale rosc.) and red ginger (Zingiber officinale var. rubrum) simplicia through washing time, slice thickness and raw materials drying process optimization. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2017;7:15–21. doi: 10.18517/ijaseit.7.1.910. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

