Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa) Mediates Anti-Oxidative Effects by Reduction of Nitric Oxide, iNOS Protein-, and mRNA-Synthesis in BV2 Microglial Cells
- PMID: 35164047
- PMCID: PMC8840760
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030784
Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa) Mediates Anti-Oxidative Effects by Reduction of Nitric Oxide, iNOS Protein-, and mRNA-Synthesis in BV2 Microglial Cells
Abstract
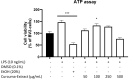
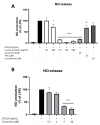
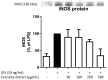
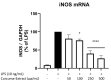
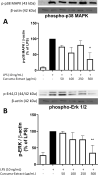
Plant-derived products have been used since the beginnings of human history to treat various pathological conditions. Practical experience as well as a growing body of research suggests the benefits of the use of turmeric (Curcuma longa) and some of its active components in the reduction of oxidative stress, a mechanism leading to neurodegeneration. In this current study, we investigated the effects of a preparation of Curcuma longa, and its constituents curcumin, tetrahydrocurcumin, and curcumenol, in one of the molecular pathways leading to oxidative stress, which is the release of NO, a free radical involved in stress conditions, using the BV2 microglial cell line. The concentration-dependent reduction of NO is linked to reduced amounts of iNOS protein- and mRNA-synthesis and is possibly mediated by the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) such as p42/44 or p38 MAPK. Therefore, the use of turmeric extract is a promising therapeutic option for diseases linked to the dysregulation of oxidative stress, with fewer side-effects in comparison to the currently used pharmacotherapeutics.
Keywords: BV2; NO; curcuma; curcumin; iNOS; microglia; oxidative stress; turmeric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The protective effect of fermented Curcuma longa L. on memory dysfunction in oxidative stress-induced C6 gliomal cells, proinflammatory-activated BV2 microglial cells, and scopolamine-induced amnesia model in mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jul 17;17(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1880-3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28716085 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumenol isolated from Curcuma zedoaria suppresses Akt-mediated NF-κB activation and p38 MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells.Food Funct. 2015 Nov;6(11):3550-9. doi: 10.1039/c5fo00607d. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Food Funct. 2015. PMID: 26301513
-
Methanol extract of Ficus leaf inhibits the production of nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated microglia via the MAPK pathway.Phytother Res. 2008 Aug;22(8):1064-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2442. Phytother Res. 2008. PMID: 18546149
-
Experimental and clinical reports on anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of Curcuma longa and curcumin, an updated and comprehensive review.Biofactors. 2021 May;47(3):311-350. doi: 10.1002/biof.1716. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Biofactors. 2021. PMID: 33606322 Review.
-
The ameliorative effect of turmeric (Curcuma longa Linn) extract and its major constituent, curcumin, and its analogs on ethanol toxicity.Phytother Res. 2024 May;38(5):2165-2181. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8165. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 38396341 Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin Attenuates Hyperglycemia and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Quantitative Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 30;16(23):4177. doi: 10.3390/nu16234177. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683570 Free PMC article.
-
The ethanolic extract of Curcuma longa grown in Korea exhibits anti-neuroinflammatory effects by activating of nuclear transcription factor erythroid-2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Dec 30;22(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03825-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 36585647 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary and Alternative Therapies in Oncology.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 21;19(9):5071. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095071. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Thai Traditional Hand and Foot Soaking Formulary and Its Bioactive Compounds.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 13;17(7):907. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070907. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733115 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress by targeting GPR55 - new approaches in the treatment of psychiatric disorders.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Dec;29(12):3779-3788. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02614-5. Epub 2024 May 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38796643 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prasad S., Aggarwal B.B. Turmeric, the Golden Spice: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Medicine. In: Benzie I.F.F., Wachtel-Galor S., editors. Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2011. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

