A Multiwell-Based Assay for Screening Thyroid Hormone Signaling Disruptors Using thibz Expression as a Sensitive Endpoint in Xenopus laevis
- PMID: 35164063
- PMCID: PMC8838645
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030798
A Multiwell-Based Assay for Screening Thyroid Hormone Signaling Disruptors Using thibz Expression as a Sensitive Endpoint in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
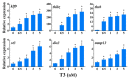
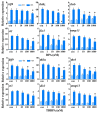
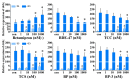
There is a need for rapidly screening thyroid hormone (TH) signaling disruptors in vivo considering the essential role of TH signaling in vertebrates. We aimed to establish a rapid in vivo screening assay using Xenopus laevis based on the T3-induced Xenopus metamorphosis assay we established previously, as well as the Xenopus Eleutheroembryonic Thyroid Assay (XETA). Stage 48 tadpoles were treated with a series of concentrations of T3 in 6-well plates for 24 h and the expression of six TH-response genes was analyzed for choosing a proper T3 concentration. Next, bisphenol A (BPA) and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), two known TH signaling disruptors, were tested for determining the most sensitive TH-response gene, followed by the detection of several suspected TH signaling disruptors. We determined 1 nM as the induction concentration of T3 and thibz expression as the sensitive endpoint for detecting TH signaling disruptors given its highest response to T3, BPA, and TBBPA. And we identified betamipron as a TH signaling agonist, and 2,2',4,4'-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) as a TH signaling antagonist. Overall, we developed a multiwell-based assay for rapidly screening TH signaling disruptors using thibz expression as a sensitive endpoint in X. laevis.
Keywords: Xenopus laevis; multiwell plate; screening assay; thibz gene; thyroid hormone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

