Inhibition of Glutamate Release from Rat Cortical Nerve Terminals by Dehydrocorydaline, an Alkaloid from Corydalis yanhusuo
- PMID: 35164225
- PMCID: PMC8838318
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27030960
Inhibition of Glutamate Release from Rat Cortical Nerve Terminals by Dehydrocorydaline, an Alkaloid from Corydalis yanhusuo
Abstract
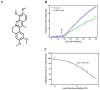
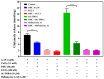
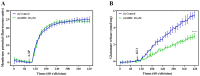
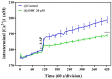
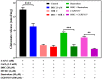
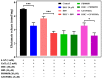
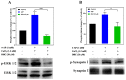
Excessive release of glutamate induces excitotoxicity and causes neuronal damage in several neurodegenerative diseases. Natural products have emerged as potential neuroprotective agents for preventing and treating neurological disorders. Dehydrocorydaline (DHC), an active alkaloid compound isolated from Corydalis yanhusuo, possesses neuroprotective capacity. The present study investigated the effect of DHC on glutamate release using a rat brain cortical synaptosome model. Our results indicate that DHC inhibited 4-aminopyridine (4-AP)-evoked glutamate release and elevated intrasynaptosomal calcium levels. The inhibitory effect of DHC on 4-AP-evoked glutamate release was prevented in the presence of the vesicular transporter inhibitor bafilomycin A1 and the N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channel blocker ω-conotoxin MVIIC but not the intracellular inhibitor of Ca2+ release dantrolene or the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger inhibitor CGP37157. Moreover, the inhibitory effect of DHC on evoked glutamate release was prevented by the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) inhibitor PD98059. Western blotting data in synaptosomes also showed that DHC significantly decreased the level of ERK1/2 phosphorylation and synaptic vesicle-associated protein synapsin I, the main presynaptic target of ERK. Together, these results suggest that DHC inhibits presynaptic glutamate release from cerebrocortical synaptosomes by suppressing presynaptic voltage-dependent Ca2+ entry and the MAPK/ERK/synapsin I signaling pathway.
Keywords: Ca2+ influx; MAPK/ERK/synapsin I; dehydrocorydaline; glutamate release; neuroprotection; synaptosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Typhaneoside Suppresses Glutamate Release Through Inhibition of Voltage-Dependent Calcium Entry in Rat Cerebrocortical Nerve Terminals.Chem Res Toxicol. 2021 May 17;34(5):1286-1295. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00446. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Chem Res Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33621091
-
Cyanocobalamin, vitamin B12, depresses glutamate release through inhibition of voltage-dependent Ca2+ influx in rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals (synaptosomes).Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Jan 14;602(2-3):230-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.11.059. Epub 2008 Dec 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19073169
-
HTDP-2, a new synthetic compound, inhibits glutamate release through reduction of voltage-dependent Ca²⁺ influx in rat cerebral cortex nerve terminals.Pharmacology. 2011;88(1-2):26-32. doi: 10.1159/000328774. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Pharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21720189
-
Neuroprotective Role of the B Vitamins in the Modulation of the Central Glutamatergic Neurotransmission.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2022;21(4):292-301. doi: 10.2174/1871527320666210902165739. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 34477538 Review.
-
Potential protective roles of phytochemicals on glutamate-induced neurotoxicity: A review.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Sep;23(9):1113-1123. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.43687.10259. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32963732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification to Unveil the Mechanism of N-Methyl-D-Aspartic Acid Rescue Humantenirine-Induced Excitotoxicity.Metabolites. 2023 Jan 28;13(2):195. doi: 10.3390/metabo13020195. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36837814 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrocorydaline attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting fibroblast activation.Respir Res. 2025 Apr 12;26(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03218-5. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40221718 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of the active Ingredients in Huanglian Jiedu decoction through amide bond-Immobilized magnetic nanoparticle-assisted cell membrane chromatography.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 19;13:1087404. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1087404. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36642988 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrocorydaline Accelerates Cell Proliferation and Extracellular Matrix Synthesis of TNFα-Treated Human Chondrocytes by Targeting Cox2 through JAK1-STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 30;23(13):7268. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137268. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806272 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating serum pharmacochemistry and network pharmacology to reveal the active constituents and mechanism of Corydalis Rhizoma in treating Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Nov 22;15:1285549. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1285549. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38076535 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

