Nanoparticles of Costus speciosus Ameliorate Diabetes-Induced Structural Changes in Rat Prostate through Mediating the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines IL 6, IL1β and TNF-α
- PMID: 35164292
- PMCID: PMC8839105
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27031027
Nanoparticles of Costus speciosus Ameliorate Diabetes-Induced Structural Changes in Rat Prostate through Mediating the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines IL 6, IL1β and TNF-α
Abstract
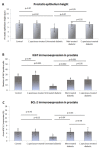
Diabetes mellitus is a common global health problem. Among the complications that are frequently associated with DM are the alternation of sexual function and fertility, especially in young men. This study aimed to assess the efficacy of nanoparticles of Costus speciosus (C. speciosus) in preserving the prostatic structure of diabetic rats and to explore the mechanism behind this effect. A model of DM was induced in male albino rats by a single intraperitoneally injection of streptozotocin (STZ, 60 mg/kg body weight). Five groups (n = 10 each) of rats were included in this study: the control, C. speciosus gold nanoparticles-treated (150 mg/kg body weight through gastric intubation for 30 days), untreated diabetic, metformin-treated diabetic (500 mg/kg/day gastric intubation for 30 days) and the C. speciosus-treated diabetic group. The blood glucose, insulin and testosterone levels as well as oxidants/antioxidants status were assessed in the serum. Gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL1β and IL-6 were assessed in the prostate homogenate. At the end of the experiment, the rats were sacrificed and the prostate was dissected out and prepared for histopathological and immunohistochemistry study using Ki67 and Bcl-2. C. Speciosus nanoparticles significantly decreased (p = 0.03) the blood glucose level while significantly increasing insulin (p = 0.01) and testosterone (p = 0.04) levels compared to the untreated diabetic rats. Oxidants/antioxidants status was markedly improved after administration of C. speciosus. Prostatic expression of the mRNA of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL1β and TNF-α was down-regulated in metformin- and C. speciosus-treated rats. The histological structure of the ventral prostate was preserved in metformin- and C. speciosus-treated diabetic rats with a significantly thicker epithelial cell layer and significant increase immunoexpression in Bcl-2 and Ki67. In conclusion, the protective effect induced by C. speciosus nanoparticles on the prostate of diabetic rats might be directly mediated through the down-regulation of inflammatory cytokines and the up-regulation of antioxidant activity and indirectly mediated through the anti-hyperglycemic effect through enhancing insulin secretion.
Keywords: Bcl-2; Costus speciosus; Ki67; cytokines; diabetes mellitus; inflammation; insulin; nanoparticles; prostate; testosterone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Miller R.G., Costacou T., Orchard T.J. Risk factor modeling for cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes in the pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications (EDC) study: A comparison with the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study (DCCT/EDIC) Diabetes. 2019;68:409–419. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rato L., Oliveira P.F., Sousa M., Silva B.M., Alves M.G. Oxidants, Antioxidants and Impact of the Oxidative Status in Male Reproduction. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Role of reactive oxygen species in diabetes-induced male reproductive dysfunction; pp. 135–147.
-
- Bais N., Choudhary G. Recent updates on natural compounds in treatment of diabetes mellitus: A comprehensive Approach. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019;9:1019–1024.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

