Theoretical Modeling of Redox Potentials of Biomolecules
- PMID: 35164342
- PMCID: PMC8838479
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27031077
Theoretical Modeling of Redox Potentials of Biomolecules
Abstract
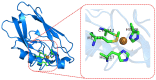
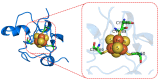
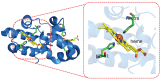
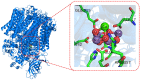
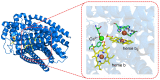
The estimation of the redox potentials of biologically relevant systems by means of theoretical-computational approaches still represents a challenge. In fact, the size of these systems typically does not allow a full quantum-mechanical treatment needed to describe electron loss/gain in such a complex environment, where the redox process takes place. Therefore, a number of different theoretical strategies have been developed so far to make the calculation of the redox free energy feasible with current computational resources. In this review, we provide a survey of such theoretical-computational approaches used in this context, highlighting their physical principles and discussing their advantages and limitations. Several examples of these approaches applied to the estimation of the redox potentials of both proteins and nucleic acids are described and critically discussed. Finally, general considerations on the most promising strategies are reported.
Keywords: DNA; proteins; redox potentials; theoretical-computational chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Vandenberghe I., Leys D., Demol H., Van Driessche G., Meyer T.E., Cusanovich M.A., Van Beeumen J. The Primary Structures of the Low-Redox Potential Diheme Cytochromescfrom the Phototrophic BacteriaRhodobacter sphaeroidesandRhodobacter adriaticusReveal a New Structural Family ofc-Type Cytochromes. Biochemistry. 1998;37:13075–13081. doi: 10.1021/bi981076z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sykes A.G. Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 1991. Active-Site Properties Of The Blue Copper Proteins; pp. 377–408. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

