Voacanga globosa Spirobisindole Alkaloids Exert Antiviral Activity in HIV Latently Infected Cell Lines by Targeting the NF-kB Cascade: In Vitro and In Silico Investigations
- PMID: 35164343
- PMCID: PMC8840767
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27031078
Voacanga globosa Spirobisindole Alkaloids Exert Antiviral Activity in HIV Latently Infected Cell Lines by Targeting the NF-kB Cascade: In Vitro and In Silico Investigations
Erratum in
-
Correction: de Jesus et al. Voacanga globosa Spirobisindole Alkaloids Exert Antiviral Activity in HIV Latently Infected Cell Lines by Targeting the NF-κB Cascade: In Vitro and In Silico Investigations. Molecules 2022, 27, 1078.Molecules. 2024 Jan 29;29(3):626. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030626. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338489 Free PMC article.
Abstract
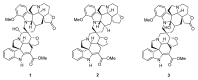
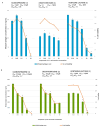
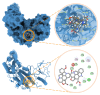
Since the efficiency in the transcription of the HIV genome contributes to the success of viral replication and infectivity, we investigated the downregulating effects of the spirobisindole alkaloids globospiramine (1), deoxyvobtusine (2), and vobtusine lactone (3) from the endemic Philippine medicinal plant, Voacanga globosa, during HIV gene transcription. Alkaloids 1-3 were explored for their inhibitory activity on TNF-α-induced viral replication in two latently HIV-infected cell lines, OM10.1 and J-Lat. The induction of HIV replication from OM10.1 and J-Lat cells elicited by TNF-α was blocked by globospiramine (1) within noncytotoxic concentrations. Furthermore, globospiramine (1) was found to target the NF-ĸB activation cascade in a dose-dependent manner when the transcriptional step at which inhibitory activity is exerted was examined in TNF-α-induced 293 human cells using transient reporter (luciferase) gene expression systems (HIV LTR-luc, ĸB-luc, and mutant ĸB-luc). Interrogation through molecular docking against the NF-ĸB p50/p65 heterodimer and target sites of the subunits comprising the IKK complex revealed high binding affinities of globospiramine (1) against the S281 pocket of the p65 subunit (BE = -9.2 kcal/mol) and the IKKα activation loop (BE = -9.1 kcal/mol). These findings suggest globospiramine (1) as a molecular inspiration to discover new alkaloid-based anti-HIV derivatives.
Keywords: HIV latency; NF-ĸB; Voacanga globosa; anti-HIV; globospiramine; spirobisindole alkaloids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- UNAIDS . Fact Sheet 2021 Global HIV Statistics. UNADIS; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021.
-
- Epidemiology Bureau . HIV/AIDS & ART Registry of the Philippines. Department of Health; Manila, Philippines: 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

