Seasonal Chemical Evaluation of Miconia chamissois Naudin from Brazilian Savanna
- PMID: 35164385
- PMCID: PMC8838837
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27031120
Seasonal Chemical Evaluation of Miconia chamissois Naudin from Brazilian Savanna
Abstract
Miconia chamissois Naudin is a species from the Cerrado, which is being increasingly researched for its therapeutic potential. The aim of this study was to obtain a standardized extract and to evaluate seasonal chemical variations. Seven batches of aqueous extracts from leaves were produced for the standardization. These extracts were evaluated for total solids, polyphenol (TPC) and flavonoid content (TFC), vitexin derivative content, antioxidant activity; thin-layer chromatography (TLC), and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) profiles were generated. For the seasonal study, leaves were collected from five different periods (May 2017 to August 2018). The results were correlated with meteorological data (global radiation, temperature, and rainfall index). Using chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques, apigenin C-glycosides (vitexin/isovitexin) and derivatives, luteolin C-glycosides (orientin/isoorientin) and derivatives, a quercetin glycoside, miconioside B, matteucinol-7-O-β-apiofuranosyl (1 → 6) -β-glucopyranoside, and farrerol were identified. Quality parameters, including chemical marker quantification by HPLC, and biological activity, are described. In the extract standardization process, all the evaluated parameters showed low variability. The seasonality study revealed no significant correlations (p < 0.05) between TPC or TFC content and meteorological data. These results showed that it is possible to obtain extracts from M. chamissois at any time of the year without significant differences in composition.
Keywords: Cerrado; Miconia chamissois Naudin; seasonality; standardized extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
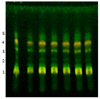
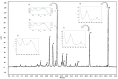

References
-
- Brasil O Bioma Cerrado. [(accessed on 10 October 2020)]; Available online: https://antigo.mma.gov.br/biomas/cerrado.
-
- Goldenberg R., Baumgratz J.F.A., Souza M.L.D.R. Taxonomia de Melastomataceae no Brasil: Retrospectiva, perspectivas e chave de identificação para os gêneros. Rodriguésia. 2012;63:145–161. doi: 10.1590/S2175-78602012000100011. - DOI
-
- Neto G.G., de Morais R.G. Recursos medicinais de espécies do Cerrado de Mato Grosso: Um estudo bibliográfico. Acta Bot. Bras. 2003;17:561–584. doi: 10.1590/S0102-33062003000400009. - DOI
-
- Goldenberg R., Caddah M.K. Miconia in Lista de Espécies da Flora do Brasil. [(accessed on 18 November 2021)]; Available online: http://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/jabot/floradobrasil/FB9683.
-
- Cruz A.V.D.M., Kaplan M.A.C. Uso medicinal de espécies das famílias Myrtaceae e Melastomataceae no Brasil. Floresta Ambiente. 2004;11:47–52.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

