Fluorogenic Detection of Human Serum Albumin Using Curcumin-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
- PMID: 35164400
- PMCID: PMC8838683
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27031133
Fluorogenic Detection of Human Serum Albumin Using Curcumin-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
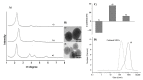
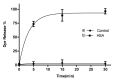
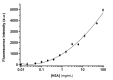
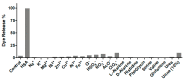
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with rhodamine B and capped with curcumin are used for the selective and sensitive fluorogenic detection of human serum albumin (HSA). The sensing mesoporous silica nanoparticles are loaded with rhodamine B, decorated with aminopropyl moieties and capped with curcumin. The nanoparticles selectively release the rhodamine B cargo in the presence of HSA. A limit of detection for HSA of 0.1 mg/mL in PBS (pH 7.4)-acetonitrile 95:5 v/v was found, and the sensing nanoparticles were used to detect HSA in spiked synthetic urine samples.
Keywords: HSA detection; gated hybrid materials; mesoporous silica; sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Liu X., Song D.Q., Zhang Q.L., Tian Y., Liu Z.Y., Zhang H.Q. Characterization of drug-binding levels to serum albumin using a wavelength modulation surface plasmon resonance sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006;117:188–195. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.11.023. - DOI
-
- Amin R., Widmer B., Prevost A.T., Schwarze P., Coope J., Edge J., Marcovecchio L., Neil A., Dalton R.N., Dunger D.B. Risk of microalbuminuria and progression to macroalbuminuria in a cohort with childhood onset type 1 diabetes: Prospective observational study. Br. Med. J. 2008;336:697–701. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39478.378241.BE. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

