Alpha B-Crystallin in Muscle Disease Prevention: The Role of Physical Activity
- PMID: 35164412
- PMCID: PMC8840510
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27031147
Alpha B-Crystallin in Muscle Disease Prevention: The Role of Physical Activity
Abstract
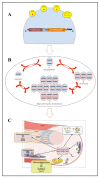
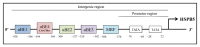
HSPB5 or alpha B-crystallin (CRYAB), originally identified as lens protein, is one of the most widespread and represented of the human small heat shock proteins (sHSPs). It is greatly expressed in tissue with high rates of oxidative metabolism, such as skeletal and cardiac muscles, where HSPB5 dysfunction is associated with a plethora of human diseases. Since HSPB5 has a major role in protecting muscle tissues from the alterations of protein stability (i.e., microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate filament components), it is not surprising that this sHSP is specifically modulated by exercise. Considering the robust content and the protective function of HSPB5 in striated muscle tissues, as well as its specific response to muscle contraction, it is then realistic to predict a specific role for exercise-induced modulation of HSPB5 in the prevention of muscle diseases caused by protein misfolding. After offering an overview of the current knowledge on HSPB5 structure and function in muscle, this review aims to introduce the reader to the capacity that different exercise modalities have to induce and/or activate HSPB5 to levels sufficient to confer protection, with the potential to prevent or delay skeletal and cardiac muscle disorders.
Keywords: alpha B-crystallin; exercise; muscle diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Human 343delT HSPB5 Chaperone Associated with Early-onset Skeletal Myopathy Causes Defects in Protein Solubility.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 15;291(29):14939-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.730481. Epub 2016 May 19. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27226619 Free PMC article.
-
The role of αB-crystallin in skeletal and cardiac muscle tissues.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018 Jul;23(4):491-505. doi: 10.1007/s12192-017-0866-x. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018. PMID: 29190034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The early response of αB-crystallin to a single bout of aerobic exercise in mouse skeletal muscles depends upon fiber oxidative features.Redox Biol. 2019 Jun;24:101183. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101183. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30974319 Free PMC article.
-
HSPB5 (αB-crystallin) confers protection against paraquat-induced oxidative stress at the organismal level in a tissue-dependent manner.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021 Jan;26(1):229-239. doi: 10.1007/s12192-020-01171-4. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021. PMID: 33078332 Free PMC article.
-
Cell biological roles of αB-crystallin.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014 Jul;115(1):3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.02.005. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24576798 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Proteomics in Obesity: Unpacking the Molecular Puzzle.Curr Obes Rep. 2024 Sep;13(3):403-438. doi: 10.1007/s13679-024-00561-4. Epub 2024 May 4. Curr Obes Rep. 2024. PMID: 38703299 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual size dimorphism in mammals is associated with changes in the size of gene families related to brain development.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 24;15(1):6257. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50386-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39048570 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Diversity of Mammalian Small Heat Shock Proteins: A Review.Cells. 2023 Jul 27;12(15):1947. doi: 10.3390/cells12151947. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37566026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Heritable Myopathies on Gastrointestinal Skeletal Muscle Function.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;19(8):101522. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2025.101522. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40268053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Mutated MYOT and CRYAB Genes Cause a Myopathic Phenotype in Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 14;24(14):11483. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411483. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511242 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

