Racial Differences in XO (Xanthine Oxidase) and Mitochondrial DNA Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Resistant Hypertension
- PMID: 35164526
- PMCID: PMC10652275
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18298
Racial Differences in XO (Xanthine Oxidase) and Mitochondrial DNA Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Resistant Hypertension
Abstract
Background: We previously reported increased plasma XO (xanthine oxidase) activity in patients with resistant hypertension. Increased XO can cause mitochondrial DNA damage and promote release of fragments called mitochondrial DNA damage-associated molecular patterns (mtDNA DAMPs). Here, we report racial differences in XO activity and mtDNA DAMPs in Black and White adults with resistant hypertension.
Methods: This retrospective study includes 91 resistant hypertension patients (44% Black, 47% female) with blood pressure >140/90 mm Hg on ≥4 medications and 37 normotensive controls (30% Black, 54% female) with plasma XO activity, mtDNA DAMPs, and magnetic resonance imaging of left ventricular morphology and function.
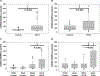
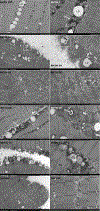
Results: Black-resistant hypertension patients were younger (mean age 52±10 versus 59±10 years; P=0.001), with higher XO activity and left ventricular wall thickness, and worse diastolic dysfunction than White resistant hypertension patients. Urinary sodium excretion (mg/24 hour per kg) was positively related to left ventricular end-diastolic volume (r=0.527, P=0.001) and left ventricular mass (r=0.394, P=0.02) among Black but not White resistant hypertension patients. Patients with resistant hypertension had increased mtDNA DAMPs versus controls (P<0.001), with Black mtDNA DAMPS greater than Whites (P<0.001). Transmission electron microscopy of skeletal muscle biopsies in resistant hypertension patients demonstrates mitochondria cristae lysis, myofibrillar loss, large lipid droplets, and glycogen accumulation.
Conclusions: These data warrant a large study to examine the role of XO and mitochondrial mtDNA DAMPs in cardiac remodeling and heart failure in Black adults with resistant hypertension.
Keywords: biopsy; blood pressure; hypertension; mitochondria; xanthine oxidase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma xanthine oxidase activity is related to increased sodium and left ventricular hypertrophy in resistant hypertension.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Apr;134:343-349. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.01.029. Epub 2019 Jan 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30695690 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen radical-induced mitochondrial DNA damage and repair in pulmonary vascular endothelial cell phenotypes.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001 Jun;280(6):L1300-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.6.L1300. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11350811
-
Xanthine oxidase inhibition preserves left ventricular systolic but not diastolic function in cardiac volume overload.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Nov 15;305(10):H1440-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00007.2013. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24014679 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA damage triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in oxidant-challenged lung endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005 Mar;288(3):L530-5. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00255.2004. Epub 2004 Nov 24. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15563690
-
Inhibitors of Xanthine Oxidase: Scaffold Diversity and Structure-Based Drug Design.ChemMedChem. 2019 Apr 3;14(7):714-743. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201900034. Epub 2019 Mar 5. ChemMedChem. 2019. PMID: 30740924 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial reactivity following acute exposure to experimental pain testing in people with HIV and chronic pain.Mol Pain. 2023 Jan-Dec;19:17448069231195975. doi: 10.1177/17448069231195975. Mol Pain. 2023. PMID: 37542365 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of co-exposure of microplastics and lead in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus).Front Vet Sci. 2023 Oct 6;10:1279382. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1279382. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37869502 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation markers associated with symptoms and neighborhood deprivation in black adults with heart failure.Heart Lung. 2025 Jul 9;74:121-128. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2025.07.001. Online ahead of print. Heart Lung. 2025. PMID: 40639059
-
Maternal nano-titanium dioxide inhalation exposure alters placental cyclooxygenase and oxidant balance in a sexually dimorphic manner.Adv Redox Res. 2024 Apr;10:10.1016/j.arres.2023.100090. doi: 10.1016/j.arres.2023.100090. Adv Redox Res. 2024. PMID: 38562524 Free PMC article.
-
High-risk alcohol consumption is associated with mitochondrial damage-associated molecular patterns in people living with HIV.Drug Alcohol Depend Rep. 2025 Jul 3;16:100359. doi: 10.1016/j.dadr.2025.100359. eCollection 2025 Sep. Drug Alcohol Depend Rep. 2025. PMID: 40687391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Delling FN, Deo R, et al.; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e67–e492. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fernandes-Silva MM, Shah AM, Hegde S, Goncalves A, Claggett B, Cheng S, Nadruz W, Kitzman DW, Konety SH, Matsushita K, et al. Race-related differences in left ventricular structural and functional remodeling in response to increased afterload: the ARIC study. JACC Heart Fail. 2017;5:157–165. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2016.10.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

