m6A modification: recent advances, anticancer targeted drug discovery and beyond
- PMID: 35164788
- PMCID: PMC8842557
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01510-2
m6A modification: recent advances, anticancer targeted drug discovery and beyond
Abstract
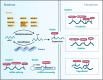
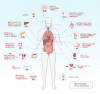
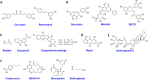
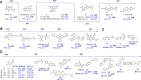
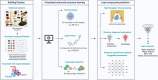
Abnormal N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is closely associated with the occurrence, development, progression and prognosis of cancer, and aberrant m6A regulators have been identified as novel anticancer drug targets. Both traditional medicine-related approaches and modern drug discovery platforms have been used in an attempt to develop m6A-targeted drugs. Here, we provide an update of the latest findings on m6A modification and the critical roles of m6A modification in cancer progression, and we summarize rational sources for the discovery of m6A-targeted anticancer agents from traditional medicines and computer-based chemosynthetic compounds. This review highlights the potential agents targeting m6A modification for cancer treatment and proposes the advantage of artificial intelligence (AI) in the discovery of m6A-targeting anticancer drugs. Three stages of m6A-targeting anticancer drug discovery: traditional medicine-based natural products, modern chemical modification or synthesis, and artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted approaches for the future.
Keywords: Cancer; Chemosynthesis; Drug discovery; Modulators; Natural product; m6A.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory effects of natural products on N6-methyladenosine modification: A novel therapeutic strategy for cancer.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Feb;29(2):103875. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103875. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 38176674 Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in cancer therapeutic resistance: Potential mechanisms and clinical implications.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115477. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115477. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37696088 Review.
-
Roles of RNA Methylations in Cancer Progression, Autophagy, and Anticancer Drug Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 20;24(4):4225. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044225. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Advances in the Roles of N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Ovarian Cancer.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241256819. doi: 10.1177/10732748241256819. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 38755968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in crosstalk between N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and circular RNAs in cancer.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Jan 21;27:947-955. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.01.013. eCollection 2022 Mar 8. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35211355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N6-methyladenosine of TRIM27 enhances the stem cell-type phenotype of cisplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 Nov 9;36:101572. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101572. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 38024865 Free PMC article.
-
M6AREG: m6A-centered regulation of disease development and drug response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D1333-D1344. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac801. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36134713 Free PMC article.
-
NOVA2 regulates the properties of liver cancer stem cells and lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the Wnt pathway.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Aug 31;15(4):1674-1685. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-145. Epub 2024 Aug 1. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39279925 Free PMC article.
-
METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?Open Med (Wars). 2023 Nov 30;18(1):20230856. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0856. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 38045858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modification of m6A regulator proteins in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2023 Jun 30;22(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01810-1. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37391814 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wiener D, Schwartz S. The epitranscriptome beyond m(6)a. Nat Rev Genet. 2021;22:119–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

