Tumor necrosis factor alpha neutralization attenuates immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced activation of intermediate monocytes in synovial fluid mononuclear cells from patients with inflammatory arthritis
- PMID: 35164829
- PMCID: PMC8842914
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02737-6
Tumor necrosis factor alpha neutralization attenuates immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced activation of intermediate monocytes in synovial fluid mononuclear cells from patients with inflammatory arthritis
Abstract
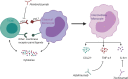
Objective: During treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) such as the anti-PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab, half of patients with pre-existing inflammatory arthritis experience disease flares. The underlying immunological mechanisms have not been characterized. Here, we investigate the effect of pembrolizumab on cells involved in inflammation and destruction in the synovial joint and how immunosuppressive treatments affect the pembrolizumab-induced immune reactions.
Methods: We included synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMCs, n = 28) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs, n = 6) from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and peripheral spondyloarthritis and PBMCs from healthy controls (n = 6). Fibroblast-like synovial cells (FLSs) were grown from SFMCs. The in vitro effect of pembrolizumab was tested in SFMCs cultured for 48 h, FLS-PBMC co-cultures and in SFMCs cultured for 21 days (inflammatory osteoclastogenesis). Cells and supernatants were analyzed by ELISA, flow cytometry, and pro-inflammatory multiplex assay. Finally, the effect of the disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) adalimumab (TNFα inhibitor), tocilizumab (IL-6R inhibitor), tofacitinib (JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor), and baricitinib (JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor) on pembrolizumab-induced immune reactions was tested.
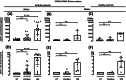
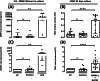
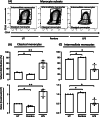
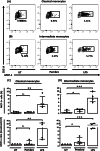
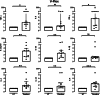
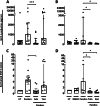
Results: Pembrolizumab significantly increased monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) production by arthritis SFMCs (P = 0.0031) but not by PBMCs from patients or healthy controls (P = 0.77 and P = 0.43). Pembrolizumab did not alter MMP-3 production in FLS-PBMC co-cultures (P = 0.76) or TRAP secretion in the inflammatory osteoclastogenesis model (P = 0.28). In SFMCs, pembrolizumab further increased the production of TNFα (P = 0.0110), IFNγ (P = 0.0125), IL-12p70 (P = 0.0014), IL-10 (P = 0.0100), IL-13 (P = 0.0044), IL-2 (P = 0.0066), and IL-4 (P = 0.0008) but did not change the production of IL-6 (P = 0.1938) and IL-1 (P = 0.1022). The SFMCs treated with pembrolizumab showed an increased frequency of intermediate monocytes (P = 0.044), and the MCP-1 production increased only within the intermediate monocyte subset (P = 0.028). Lastly, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib treatment were able to attenuate the pembrolizumab-induced MCP-1 production (P = 0.0004, P = 0.033, and P = 0.025, respectively), while this was not seen with tocilizumab treatment (P = 0.75).
Conclusion: Pembrolizumab specifically activated intermediate monocytes and induced the production of several cytokines including TNFα but not IL-6. These findings indicate that flares in patients with pre-existing inflammatory arthritis involve monocyte activation and could be managed with TNFα neutralization.
Keywords: Arthritis; Cytokine; Immunotherapy; Monocyte.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TWK has engaged in educational activities presenting in topics on immunology in rheumatic diseases receiving speaking fees from Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and UCB and has received a consultancy fee from Bristol-Myers Squibb. TWK is co-founder and clinical developer in iBiotech ApS developing diagnostic and therapeutic solutions for people with autoimmune diseases and cancer. TV-J taught in a training course for health care professionals on the side effects of ICIs and was paid an honorarium by Roche. The rest of the authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitro-fatty acids decrease type I interferons and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in ex vivo models of inflammatory arthritis.BMC Immunol. 2021 Dec 17;22(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12865-021-00471-3. BMC Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34920714 Free PMC article.
-
Responses to Cytokine Inhibitors Associated with Cellular Composition in Models of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Arthritis.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020 Jan;2(1):3-10. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11094. Epub 2019 Nov 11. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31943973 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Galectin-9 Levels Correlate with Disease Activity in Patients with DMARD-Naïve Rheumatoid Arthritis and Modulate the Secretion of MCP-1 and IL-6 from Synovial Fibroblasts.Cells. 2023 Jan 15;12(2):327. doi: 10.3390/cells12020327. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672263 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating and Synovial Monocytes in Arthritis and Ex-Vivo Model to Evaluate Therapeutic Modulation of Synovial Monocytes.Immunol Invest. 2023 Nov;52(7):832-855. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2247438. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 37615125 Review.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Associated Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024 Nov 26;27(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s11926-024-01173-6. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39589663 Review.
Cited by
-
Atezolizumab Induces Necroptosis and Contributes to Hepatotoxicity of Human Hepatocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 20;24(14):11694. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411694. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511454 Free PMC article.
-
The Mitigating Effect of Combined Glucocorticoids with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors on Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3 and Programmed Death-1 Expression.Eur J Immunol. 2025 Aug;55(8):e70033. doi: 10.1002/eji.70033. Eur J Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40788332 Free PMC article.
-
Target Role of Monocytes as Key Cells of Innate Immunity in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Diseases. 2024 Apr 25;12(5):81. doi: 10.3390/diseases12050081. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 38785736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocyte-related markers as predictors of immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy and immune-related adverse events: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025 Feb 21;44(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s10555-025-10246-6. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025. PMID: 39982537 Free PMC article.
-
The JAK-STAT Pathway as a Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;16(3):611. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030611. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

