Efficacy and safety of modified Bushen Yiqi formulas (MBYF) as an add-on to formoterol and budesonide in the management of COPD: study protocol for a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, randomized clinical trial: FB-MBYF Trial
- PMID: 35164853
- PMCID: PMC8842909
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-022-06057-7
Efficacy and safety of modified Bushen Yiqi formulas (MBYF) as an add-on to formoterol and budesonide in the management of COPD: study protocol for a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, randomized clinical trial: FB-MBYF Trial
Abstract
Background: Inhaled glucocorticoid corticosteroid (ICS), long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonist (LABA), and other drugs have limited therapeutic effects on COPD with significant individual differences. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)-modified Bushen Yiqi formula (MBYF) demonstrates advantages in COPD management in China. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of MBYF as an add-on to budesonide/formoterol in COPD patients and confirm the related genes affecting the therapeutic effect in the treatment of COPD.
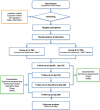
Methods: In this multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study, eligible patients with COPD will randomly receive a 360-day placebo or MBYF as an adjuvant to budesonide/formoterol in a 1:1 ratio and be followed up with every 2 months. The primary outcomes will be the frequency, times, and severity of acute exacerbation of COPD (AECOPD), COPD assessment test (CAT) score, and pulmonary function tests (PFTs). The secondary outcomes will include the modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnoea scale, 6-min walking test (6MWT), BODE index, quantitative scores of syndromes classified in TCM, inflammation indices, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenaline (HPA) axis function. We will also test the genotype to determine the relationship between drugs and efficacy. All the data will be recorded in case report forms (CRFs) and analysed by SPSS V.20.0.
Discussion: A randomized clinical trial design to evaluate the efficacy and safety of MBYF in COPD is described. The results will provide evidence for the combination therapy of modern medicine and TCM medicine, and individual therapy for COPD.
Trial registration: ID: ChiCTR1900026124 , Prospective registration.
Keywords: COPD; Design and method; Formoterol and budesonide; Randomised clinical trial; Traditional Chinese medicine formula.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- The top 10 causes of death 2018 [Available from: https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of....
-
- Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: World Health Organization; 2019 [Available from: https://www.who.int/respiratory/copd/burden/en/.
-
- Wang C, Xu J, Yang L, Xu Y, Zhang X, Bai C, Kang J, Ran P, Shen H, Wen F, Huang K, Yao W, Sun T, Shan G, Yang T, Lin Y, Wu S, Zhu J, Wang R, Shi Z, Zhao J, Ye X, Song Y, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Ding L, Yang T, Chen Y, Guo Y, Xiao F, Lu Y, Peng X, Zhang B, Xiao D, Chen CS, Wang Z, Zhang H, Bu X, Zhang X, An L, Zhang S, Cao Z, Zhan Q, Yang Y, Cao B, Dai H, Liang L, He J, China Pulmonary Health Study Group Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health CPH study): a national cross-sectional study. Lancet. 2018;391(10131):1706–1717. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30841-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, Yin P, Zhu J, Chen W, Li X, Wang L, Wang L, Liu Y, Liu J, Zhang M, Qi J, Yu S, Afshin A, Gakidou E, Glenn S, Krish VS, Miller-Petrie MK, Mountjoy-Venning WC, Mullany EC, Redford SB, Liu H, Naghavi M, Hay SI, Wang L, Murray CJL, Liang X. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394(10204):1145–1158. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dong F, Ren X, Huang K, Wang Y, Jiao J, Yang T. Development and validation of risk prediction model for in-hospital mortality among patients hospitalized with acute exacerbation chronic obstructive pulmonary disease between 2015 and 2019. Front Med. 2021;8:630870. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.630870. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZY (2018-2020)-CCCX-4002/Shanghai three-year Action Plan for further speeding up the Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2018-2020)
- 19401931400/Shanghai science and technology commission scientific research project
- ZYKC201601023/Collaborative Innovation Center for Modern Science and Technology and Industrial Development of Jiangxi Traditional Medicine (CN)
- 81501180/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous