Combined Perioperative Lapatinib and Trastuzumab in Early HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Identifies Early Responders: Randomized UK EPHOS-B Trial Long-Term Results
- PMID: 35165099
- PMCID: PMC9610457
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3177
Combined Perioperative Lapatinib and Trastuzumab in Early HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Identifies Early Responders: Randomized UK EPHOS-B Trial Long-Term Results
Abstract
Purpose: EPHOS-B aimed to determine whether perioperative anti-HER2 therapy inhibited proliferation and/or increased apoptosis in HER2-positive breast cancer.
Patients and methods: This randomized phase II, two-part, multicenter trial included newly diagnosed women with HER2-positive invasive breast cancer due to undergo surgery. Patients were randomized to: part 1 (1:2:2), no treatment (control), trastuzumab or lapatinib; part 2 (1:1:2) control, trastuzumab, or lapatinib and trastuzumab combination. Treatment was given for 11 days presurgery. Coprimary endpoints were change in Ki67 and apoptosis between baseline and surgery tumor samples (biologic response: ≥30% change). Central pathology review scored residual cancer burden (RCB). Relapse-free survival (RFS) explored long-term effects.
Results: Between November 2010 and September 2015, 257 patients were randomized (part 1: control 22, trastuzumab 57, lapatinib 51; part 2: control 29, trastuzumab 32, combination 66). Ki67 response was evaluable for 223 patients: in part 1 Ki67 response occurred in 29/44 (66%) lapatinib versus 18/49 (37%) trastuzumab (P = 0.007) and 1/22 (5%) control (P < 0.0001); in part 2 in 36/49 (74%) combination versus 14/31 (45%) trastuzumab (P = 0.02) and 2/28 (7%) control (P < 0.0001). No significant increase in apoptosis after 11 days was seen in treatment groups. Six patients achieved complete pathologic response (pCR, RCB0) and 13 RCB1, all but two in the combination group. After 6 years median follow-up, 28 (11%) had recurrence and 19 (7%) died. No recurrences or deaths were observed among patients who achieved a pCR. Ki67% falls ≥50% associated with fewer recurrences (P = 0.002).
Conclusions: Early response after short duration anti-HER2 dual therapy identifies cancers dependent on the HER2 pathway providing a strategy for exploring risk-adapted individualized treatment de-escalation.
©2022 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

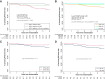
![Figure 2. Percentage change in Ki67 between pretreatment (baseline) and surgery for part 1 (A) and part 2 (B); Kaplan–Meier estimates by treatment group for relapse free survival (C) and overall survival (D). A, Waterfall plots for part 1 and part 2: for each patient, bar height represents percentage change at surgery from baseline. Percentage change was calculated as [(surgery score + 0.1) − (pretreatment score + 0.1)]/[(pretreatment score + 0.1)]*100. The constant of 0.1 was added to accommodate cases with a value of 0%. Negative values represent decrease from baseline, positive values represent increase from baseline. pCR in breast: patients with pCR (no disease in ether breast or nodes) plus two additional patients with 0% breast cellularity but nodal involvement are represented as bars of height −120% at the left of the figures and noted “pCR in breast;” any existing Ki67 values for these patients have been excluded of the main analysis; in a sensitivity analysis, we imputed a value of −100% change for these patients (Appendix 2). Small triangles indicate patients with RCB1. Disease recurrences are also indicated at the top of each figure with circles and crosses. B, RFS is represented in the time interval of up to 6 years after randomization, as no RFS event occurred later. Overall survival is represented in the fully observed range of values. Log-rank test comparing concurrently randomized treatment groups are reported in the figures. In the figure, trastuzumab and control part 1 and part 2 groups are combined to improve readability. C, control; L, lapatinib; T, trastuzumab; T+L, combination; P1, part 1; P2, part 2; all, P1&P2; P, P value.](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/5212/9610457/c54d4655ba33/1323fig2.gif)
References
-
- Rimawi MF, Mayer IA, Forero A, Nanda R, Goetz MP, Rodriguez AA, et al. Multicenter phase II study of neoadjuvant lapatinib and trastuzumab with hormonal therapy and without chemotherapy in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-overexpressing breast cancer: TBCRC 006. J Clin Oncol 2013;31:1726–31. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guarneri V, Dieci MV, Frassoldati A, Maiorana A, Ficarra G, Bettelli S, et al. Prospective biomarker analysis of the randomized CHER-LOB Study evaluating the dual Anti-HER2 treatment with trastuzumab and lapatinib plus chemotherapy as neoadjuvant therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. Oncologist 2015;20:1001–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumler I, Tuxen MK, Nielsen DL. A systematic review of dual targeting in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 2014;40:259–70. - PubMed
-
- Leary A, Evans A, Johnston SRD, A'Hern R, Bliss JM, Sahoo R, et al. Antiproliferative effect of lapatinib in HER2-positive and HER2-negative/HER3-high breast cancer: results of the presurgical randomized MAPLE Trial (CRUK E/06/039). Clin Cancer Res 2015;21:2932–40. - PubMed
-
- Dowsett M, Bundred NJ, Decensi A, Sainsbury RC, Lu Y, Hills MJ, et al. Effect of raloxifene on breast cancer cell Ki67 and apoptosis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial in postmenopausal patients. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2001;10:961–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

