Praluzatamab Ravtansine, a CD166-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors: An Open-Label Phase I/II Trial
- PMID: 35165101
- PMCID: PMC9365353
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3656
Praluzatamab Ravtansine, a CD166-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors: An Open-Label Phase I/II Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Praluzatamab ravtansine (CX-2009) is a conditionally activated Probody drug conjugate (PDC) comprising an anti-CD166 mAb conjugated to DM4, with a protease-cleavable linker and a peptide mask that limits target engagement in normal tissue and circulation. The tumor microenvironment is enriched for proteases capable of cleaving the linker, thereby releasing the mask, allowing for localized binding of CX-2009 to CD166. CX-2009 was evaluated in a phase I/II clinical trial for patients with advanced solid tumors.
Patients and methods: Eligible patients had metastatic cancer receiving ≥2 prior treatments. CX-2009 was administered at escalating doses every 3 weeks (0.25-10 mg/kg) or every 2 weeks (4-6 mg/kg). Primary objective was to determine the safety profile and recommended phase II dose (RP2D).
Results: Of 99 patients enrolled, the most prevalent subtype was breast cancer (n = 45). Median number of prior therapies was 5 (range, 1-19). Dose-limiting toxicities were observed at 8 mg/kg every 3 weeks and 6 mg/kg every 2 weeks. On the basis of tolerability, the RP2D was 7 mg/kg every 3 weeks. Tumor regressions were observed at doses ≥4 mg/kg. In the hormone receptor-positive/HER2-nonamplified breast cancer subset (n = 22), 2 patients (9%) had confirmed partial responses, and 10 patients (45%) had stable disease. Imaging with zirconium-labeled CX-2009 confirmed uptake in tumor lesions and shielding of major organs. Activated, unmasked CX-2009 was measurable in 18 of 22 posttreatment biopsies.
Conclusions: CD166 is a novel, ubiquitously expressed target. CX-2009 is the first conditionally activated antibody-drug conjugate to CD166 to demonstrate both translational and clinical activity in a variety of tumor types.
©2022 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
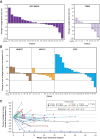
![Figure 1. [89Zr]Zr-CX-2009 evaluation and comparison with mAbs evaluated in previous clinical studies (baseline). A, A total of 10 mg, 37 MBq of [89Zr]Zr-CX-2009 was administered to a patient with micropapillary adenocarcinoma of the lung. B, Using Patlak analysis, irreversible uptake (Ki) of [89Zr]Zr-CX-2009 in major organs was compared with a validated set of four mAbs. C, Tumor uptake was confirmed in this tumor type with low cellularity (images 162 hours after injection, top = (18F)FDG, bottom = [89Zr]Zr-CX-2009, left images = PET/CT fusion, middle = CT scan in lung setting, right = PET). A tumor lesion in the left lower lung is indicated with a blue circle. Note: additional tumor tissue is present in the right lower lung. However, due to the close proximity of this lesion with the liver, uptake of [89Zr]Zr-CX-2009 is not reliably distinguishable.](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/8b7d/9365353/0d57053e682a/2020fig1.gif)

References
-
- Desnoyers LR, Vasiljeva O, Richardson JH, Yang A, Menendez EEM, Liang TW, et al. Tumor-specific activation of an EGFR-targeting probody enhances therapeutic index. Sci Transl Med 2013;5:207ra144. - PubMed
-
- Polu KR, Lowman HB. Probody therapeutics for targeting antibodies to diseased tissue. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2014;14:1049–53. - PubMed
-
- Weidle UH, Eggle D, Klostermann S, Swart GWM. ALCAM/CD166: cancer-related issues. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2010;7:231–43. - PubMed
-
- Bouchard H, Viskov C, Garcia-Echeverria C. Antibody-drug conjugates—a new wave of cancer drugs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2014;24:5357–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

