The anti-inflammatory effects of Akkermansia muciniphila and its derivates in HFD/CCL4-induced murine model of liver injury
- PMID: 35165344
- PMCID: PMC8844054
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-06414-1
The anti-inflammatory effects of Akkermansia muciniphila and its derivates in HFD/CCL4-induced murine model of liver injury
Abstract
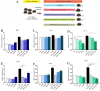
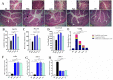
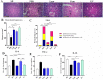
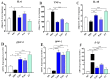
Inflammation plays a critical role in the promotion of hepatocyte damage and liver fibrosis. In recent years the protective role of Akkermansia muciniphila, a next-generation beneficial microbe, has been suggested for metabolic and inflammatory disorders. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of live and pasteurized A. muciniphila and its extra cellular vesicles (EVs) on inflammatory markers involved in liver fibrosis in a mouse model of a high-fat diet (HFD)/carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury. Firstly, the responses of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) to live and pasteurized A. muciniphila and its EVs were examined in the quiescent and LPS-activated LX-2 cells. Next, the anti-inflammatory effects of different forms of A. muciniphila were examined in the mouse model of HFD/CCl4-induced liver injury. The gene expression of various inflammatory markers was evaluated in liver, colon, and white adipose tissues. The cytokine secretion in the liver and white adipose tissues was also measured by ELISA. The results showed that administration of live and pasteurized A. muciniphila and its EVs leads to amelioration in HSCs activation. Based on data obtained from the histopathological analysis, an improvement in gut health was observed through enhancing the epithelium and mucosal layer thickness and strengthening the intestinal integrity in all treatments. Moreover, live A. muciniphila and its EVs had inhibitory effects on liver inflammation and hepatocytes damage. In addition, the tissue cytokine production and inflammatory gene expression levels revealed that live A. muciniphila and its EVs had more pronounced anti-inflammatory effects on liver and adipose tissues. Furthermore, EVs had better effects on the modulation of gene expression related to TLRs, PPARs, and immune response in the liver. In conclusion, the present results showed that oral administration of A. muciniphila and its derivatives for four weeks could enhance the intestinal integrity and anti-inflammatory responses of the colon, adipose, and liver tissues and subsequently prevent liver injury in HFD/CCL4 mice.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Protective Effects of Live and Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila and Its Extracellular Vesicles against HFD/CCl4-Induced Liver Injury.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0048421. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00484-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34549998 Free PMC article.
-
The beneficial effects of Akkermansia muciniphila and its derivatives on pulmonary fibrosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Nov;180:117571. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117571. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39418965
-
Extracellular vesicles and pasteurized cells derived from Akkermansia muciniphila protect against high-fat induced obesity in mice.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Dec 4;20(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01709-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 34863163 Free PMC article.
-
Akkermansia muciniphila as a Next-Generation Probiotic in Modulating Human Metabolic Homeostasis and Disease Progression: A Role Mediated by Gut-Liver-Brain Axes?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3900. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043900. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Akkermansia muciniphila on Improving Gut and Metabolic Health Modulation: A Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Mouse Model Studies.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 9;12(8):1627. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081627. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203469 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The potential impact of a probiotic: Akkermansia muciniphila in the regulation of blood pressure-the current facts and evidence.J Transl Med. 2022 Sep 24;20(1):430. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03631-0. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36153618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akkermansia muciniphila as a Potential Guardian against Oral Health Diseases: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 12;16(18):3075. doi: 10.3390/nu16183075. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial insights into postbiotics against colorectal cancer.Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 10;10:1111872. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1111872. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36969804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlating the Gut Microbiota and Circulating Hormones with Acne Lesion Counts and Skin Biophysical Features.Microorganisms. 2023 Aug 9;11(8):2049. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11082049. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630609 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory role of oral microbiota in inflammatory diseases and allergic conditions.Front Allergy. 2023 Feb 17;4:1067483. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2023.1067483. eCollection 2023. Front Allergy. 2023. PMID: 36873050 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

