Rapid development of an updated mRNA vaccine against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
- PMID: 35165421
- PMCID: PMC8853430
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-022-00626-w
Rapid development of an updated mRNA vaccine against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
Conflict of interest statement
C.F.Q. and B.Y. are co-inventors of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. The authors declare no competing interests.
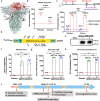
Figures
References
-
- Lu, L. et al.. Clin. Infect. Dis. ciab1041 (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

