Differential lipidomics of HK-2 cells and exosomes under high glucose stimulation
- PMID: 35165524
- PMCID: PMC8795806
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.67326
Differential lipidomics of HK-2 cells and exosomes under high glucose stimulation
Abstract
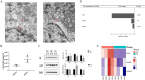
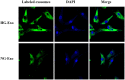
Abnormal cellular lipid metabolism has a very important role in the occurrence and progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD). However, the lipid composition and differential expression by high glucose stimulation of renal tubular cells and their exosomes, which is a vital part of the development of DKD, are largely unknown. In this study, based on targeted lipid analysis by isotope labeling and tandem mass spectrometry, a total of 421 and 218 lipid species were quantified in HK-2 cells and exosomes, respectively. More importantly, results showed that GM3 d18:1/22:0, GM3 d18:1/16:0, GM3 d18:0/16:0, GM3 d18:1/22:1 were significantly increased, while LPE18:1, LPE, CL66:4 (16:1), BMP36:3, CL70:7 (16:1), CL74:8 (16:1) were significantly decreased in high glucose-stimulated HK-2 cells. Also, PG36:1, FFA22:5, PC38:3, SM d18:1/16:1, CE-16:1, CE-18:3, CE-20:5, and CE-22:6 were significantly increased, while GM3 d18:1/24:1, GM3 were significantly decreased in exosomes secreted by high glucose-stimulated HK-2 cells. Furthermore, TAG, PC, CL were decreased significantly in the exosomes comparing with the HK-2 cells, and LPA18:2, LPI22:5, PG32:2, FFA16:1, GM3 d18:1/18:1, GM3 d18:1/20:1, GM3 d18:0/20:0, PC40:6p, TAG52:1(18:1), TAG52:0(18:0), CE-20:5, CE-20:4, CE-22:6 were only found in exosomes. In addition, the expression of PI4P in HK-2 cells decreased under a high glucose state. These data may be useful to provide new targets for exploring the mechanisms of DKD.
Keywords: Diabetic kidney disease; Exosomes; Renal tubules; Targeted lipidomics.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- G Michelle Ducasa, Alla Mitrofanova, Alessia Fornoni. Crosstalk between lipids and mitochondria in diabetic kidney disease. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2019;19:144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

