Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome From the Perspective of a Rheumatologist
- PMID: 35165550
- PMCID: PMC8830433
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.21090
Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome From the Perspective of a Rheumatologist
Abstract
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disease that can lead to thrombotic or obstetric complications. Recent histopathological studies have shown the absence of placental thrombosis, leading to the consideration of other pathophysiological pathways such as inflammation and complement activation. Due to this, various clinical studies are being carried out with different drug agents in order to avoid their complications. The combination of prophylactic heparin treatment and low doses of aspirin today result in successful pregnancies in most cases. Despite this, a minority of patients require alternative therapies to avoid recurrent miscarriage and decrease obstetric morbidity. Thanks to the better understanding of its pathophysiology, other treatments such as low doses of glucocorticoids, hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), immunoglobulin, pravastatin, and plasmapheresis have been considered in refractory cases, achieving favorable results. Despite the great advances regarding its treatment, unfortunately, there are no treatments with a good level of evidence to reduce late obstetric complications. The evaluation of preconception risk factors, as well as the antiphospholipid antibody profile, is necessary to establish individual risk and thus anticipate possible complications.
Keywords: antiphospholipid antibodies; hydroxychloroquine; obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome; placental insufficiency; thrombosis.
Copyright © 2022, Santacruz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

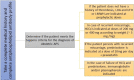
References
-
- International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Obstetric anti-phospholipid syndrome: from pathogenesis to treatment. Kaneko K, Ozawa N, Murashima A. Immunol Med. 2021:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Histopathology in the placentae of women with antiphospholipid antibodies: a systematic review of the literature. Viall CA, Chamley LW. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.01.008. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14:446–471. - PubMed
-
- Clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with isolated thrombotic vs. obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome: a prospective cohort study. Jiang H, Wang CH, Jiang N, et al. http://10.1186/s13075-021-02515-w. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23:138. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
