Novel PTH Gene Mutations Causing Isolated Hypoparathyroidism
- PMID: 35165722
- PMCID: PMC9113798
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgac086
Novel PTH Gene Mutations Causing Isolated Hypoparathyroidism
Abstract
Context: Parathyroid hormone (PTH) gene mutations represent a rare cause of familial isolated hypoparathyroidism (FIH). These defects can cause hypoparathyroidism with increased or decreased serum levels of PTH through 1) impaired PTH synthesis; 2) induction of parathyroid cell apoptosis; or 3) secretion of bioinactive PTH molecules. Eight pathogenic mutations of this gene have been described previously.
Objective: Through describing 2 novel mutations of the PTH gene, we aim to extend the molecular basis for FIH and further refine the proposed mechanisms by which PTH mutations cause hypoparathyroidism.
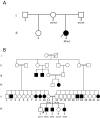
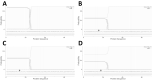
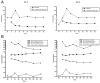
Methods: Proband case reports were compiled with extended family analysis. The probands in both kindreds presented before age 10 days with hypocalcemia and elevated phosphate levels. Proband A had low PTH levels, whereas these levels were elevated in Proband B. Proband B was initially diagnosed with pseudohypoparathyroidism. Methylation analysis was performed of CpG dinucleotides within 3 GNAS differentially methylated regions; whole-genome sequencing; and PTH infusion with analysis of nephrogenous 3',5'-cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate.
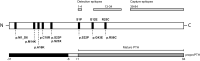
Results: Proband A had a novel heterozygous sequence change in exon 2 of the PTH gene, c.46_47delinsAA (p.Ala16Lys), and proband B had a novel homozygous nucleotide transition in PTH exon 3 (c.128G > A; p.G43E) that led to replacement of glycine by glutamic acid at position 12 of PTH 1-84. PTH 1-34 infusion demonstrated that renal responsiveness to PTH was intact and not antagonized by circulating bioinactive PTH.
Conclusion: PTH gene mutations are uncommon causes of hypoparathyroidism, but can be misdiagnosed as disorders of gland development or receptor function if PTH levels are decreased or elevated, respectively. Genetic testing should be considered early in the diagnostic approach to these presentations.
Keywords: PTH; bioinactive; genetic; hypocalcemia; hypoparathyroidism; parathyroid.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Case report: Familial hypoparathyroidism with elevated parathyroid hormone due to an inactivating PTH mutation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 7;15:1415639. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1415639. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39435356 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital Hypoparathyroidism Associated With Elevated Circulating Nonfunctional Parathyroid Hormone Due to Novel PTH Mutation.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jul 1;105(7):dgaa279. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa279. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32421798
-
Autosomal Dominant PTH Gene Signal Sequence Mutation in a Family With Familial Isolated Hypoparathyroidism.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Nov 1;102(11):3961-3969. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00250. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28938448
-
Hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism.Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1997 Aug;39(4):485-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200x.1997.tb03625.x. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1997. PMID: 9316298 Review.
-
[Differential diagnosis of hypoparathyroidism and the Ellsworth-Howard's test].Clin Calcium. 2007 Aug;17(8):1182-5. Clin Calcium. 2007. PMID: 17660613 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Rare genetic disorders that impair parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion, or bioactivity provide insights into the diagnostic utility of different parathyroid hormone assays.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2024 Jul 1;33(4):375-382. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000999. Epub 2024 May 3. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38701324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homozygous Ser-1 to Pro-1 mutation in parathyroid hormone identified in hypocalcemic patients results in secretion of a biologically inactive pro-hormone.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Feb 21;120(8):e2208047120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208047120. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36795755 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Familial hypoparathyroidism with elevated parathyroid hormone due to an inactivating PTH mutation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 7;15:1415639. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1415639. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39435356 Free PMC article.
-
Rare cause of persistent hypocalcaemia in infancy due to PTH gene mutation.BMJ Case Rep. 2023 Sep 12;16(9):e256358. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2023-256358. BMJ Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37699739
-
Quantitative hypermorphic FAM111A alleles cause autosomal recessive Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 2 and osteocraniostenosis.JCI Insight. 2025 Feb 11;10(6):e186862. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.186862. eCollection 2025 Mar 24. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 39932783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thakker RV. Diseases associated with the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor. Cell Calcium. 2004;35(3):275-282. - PubMed

