Regulation and outcomes of localized RNA translation
- PMID: 35166036
- PMCID: PMC9787767
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1721
Regulation and outcomes of localized RNA translation
Abstract
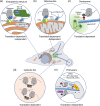
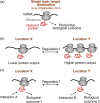
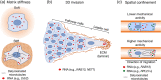
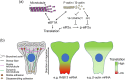
Spatial segregation of mRNAs in the cytoplasm of cells is a well-known biological phenomenon that is widely observed in diverse species spanning different kingdoms of life. In mammalian cells, localization of mRNAs has been documented and studied quite extensively in highly polarized cells, most notably in neurons, where localized mRNAs function to direct protein production at sites that are quite distant from the soma. Recent studies have strikingly revealed that a large proportion of the cellular transcriptome exhibits polarized distributions even in cells that lack an obvious need for long-range transport, such as fibroblasts or epithelial cells. This review focuses on emerging concepts regarding the functional outcomes of mRNA targeting in the cytoplasm of such cells. We also discuss regulatory mechanisms controlling these events, with an emphasis on the role of cell mechanics and the organization of the cytoskeleton. This article is categorized under: Translation > Regulation RNA Export and Localization > RNA Localization.
Keywords: RNA localization; RNA transport; cytoskeleton; local translation; mechanical signaling.
© 2022 The Authors. WIREs RNA published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. This article has been contributed to by US Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of mammalian gene expression by selective mRNA export.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jul;16(7):431-42. doi: 10.1038/nrm4010. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26081607 Review.
-
Understanding mRNA trafficking: are we there yet?Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Aug;32:63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.04.025. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24769369 Review.
-
Molecular insights into intracellular RNA localization.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2013;302:1-39. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407699-0.00001-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23351709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA transport from transcription to localized translation: a single molecule perspective.RNA Biol. 2021 Sep;18(9):1221-1237. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1842631. Epub 2020 Nov 13. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33111627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Getting the message across: the intracellular localization of mRNAs in higher eukaryotes.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:569-614. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.17.1.569. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001. PMID: 11687499 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantifying 3'UTR length from scRNA-seq data reveals changes independent of gene expression.Nat Commun. 2024 May 14;15(1):4050. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48254-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38744866 Free PMC article.
-
It's complicated: the interplay of Kif1c mRNA localization in cell protrusions, assembly of protein binding partners on the KIF1C protein, and cell migration.Genes Dev. 2023 Mar 1;37(5-6):137-139. doi: 10.1101/gad.350538.123. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 36889919 Free PMC article.
-
Centrocortin potentiates co-translational localization of its mRNA to the centrosome via dynein.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 9:2024.08.09.607365. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.09.607365. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39149256 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
CoLoC-seq probes the global topology of organelle transcriptomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Feb 22;51(3):e16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1183. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36537202 Free PMC article.
-
Subcytoplasmic location of translation controls protein output.Mol Cell. 2023 Dec 21;83(24):4509-4523.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.11.025. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 38134885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basu, S. K. , Malik, R. , Huggins, C. J. , Lee, S. , Sebastian, T. , Sakchaisri, K. , Quinones, O. A. , Alvord, W. G. , & Johnson, P. F. (2011). 3'UTR elements inhibit Ras‐induced C/EBPbeta post‐translational activation and senescence in tumour cells. The EMBO Journal, 30(18), 3714–3728. 10.1038/emboj.2011.250 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergalet, J. , Patel, D. , Legendre, F. , Lapointe, C. , Benoit Bouvrette, L. P. , Chin, A. , Blanchette, M. , Kwon, E. , & Lecuyer, E. (2020). Inter‐dependent centrosomal co‐localization of the cen and ik2 cis‐natural antisense mRNAs in Drosophila. Cell Reports, 30(10), 3339–3352. 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.047 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

