CD93 in macrophages: A novel target for atherosclerotic plaque imaging?
- PMID: 35166040
- PMCID: PMC8995462
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17237
CD93 in macrophages: A novel target for atherosclerotic plaque imaging?
Abstract
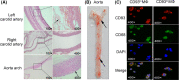
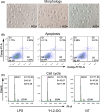
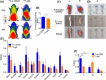
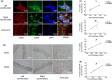
Noninvasive imaging atherosclerotic (AS) plaque is of great importance for early diagnosis. Recently, CD93 in MΦ was linked to atherosclerosis development. Herein, we have investigated whether CD93 in MΦ is a potential novel target for atherosclerotic plaque imaging. CD93hi and CD93lo MΦ were prepared with or without LPS stimulation, before biological activity was evaluated. A rat AS model was produced with left carotid artery clamped. Whole-body/ex vivo phosphor autoradiography of the artery and biodistribution were investigated after incorporation of 3 H-2-DG into CD93hi and CD93lo MΦ or after 125 I-α-CD93 (125 I-anti-CD93mAb) injection. The plaque tissue was subjected to CD93/CD68 immunofluorescence/immunohistochemistry staining. CD93hi and CD93lo MΦ cells were successfully prepared without significant effect on bioactivity after incorporative labelled with 3 H-2-DG. The AS model was successfully established. Biodistribution studies showed that adoptive transfer of 3 H-2-DG-CD93hi MΦ or 125 I- α-CD93 injection resulted in accumulation of radioactivity within the atherosclerotic plaque in the clamped left carotid artery. T/NT (target/non-target, left/right carotid artery) ratio was higher in the 3 H-2-DG-CD93hi MΦ adoptive transfer group than in the 3 H-2-DG-CD93lo MΦ group (p < .05). Plaque radioactivity in the 125 I-α-CD93 injection group was significantly higher than in the 125 I-IgG control group (p < .01). The higher radioactivity accumulated in the clamped left carotid artery was confirmed by phosphor autoradiography. More importantly, CD93/CD68 double-positive MΦ accumulated at the atherosclerotic plaque in 3 H-2-DG-CD93hi MΦ adoptive transfer group, which correlated with plaque radioactivity (r = .99, p < .01). In summary, both adoptive-transferred 3 H-2-DG-labelled CD93hi MΦ and 125 I-α-CD93 injection specifically targeted CD93 in atherosclerotic plaque. CD93 is a potential target in atherosclerotic plaque imaging.
Keywords: CD93; atherosclerosis; macrophage; molecular imaging; radionuclide.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Finn AV, Nakano M, Narula J, Kolodgie FD, Virmani R. Concept of vulnerable/unstable plaque. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. Jul;30(7):1282‐1292. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Zhang X, Song Y, et al. SPECT and fluorescence imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque with a vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 single‐chain antibody fragment. Atherosclerosis. 2016. Nov;254:263‐270. - PubMed
-
- Raggi P, Achenbach S. Computed tomography for atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease imaging. Discov Med. 2010. Feb;9(45):98‐104. - PubMed
-
- Jager NA, Westra J, Golestani R, et al. Folate receptor‐β imaging using 99mTc‐folate to explore distribution of polarized macrophage populations in human atherosclerotic plaque. J Nucl Med. 2014. Dec;55(12):1945‐1951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

