Characterization of Blood Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells in Patients With Axial Spondyloarthritis and of Resident Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells From the Axial Entheses of Non-Axial Spondyloarthritis Control Patients
- PMID: 35166073
- PMCID: PMC9825958
- DOI: 10.1002/art.42090
Characterization of Blood Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells in Patients With Axial Spondyloarthritis and of Resident Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells From the Axial Entheses of Non-Axial Spondyloarthritis Control Patients
Abstract
Objective: The importance of interleukin-17A (IL-17A) in the pathogenesis of axial spondyloarthritis (SpA) has been demonstrated by the success of IL-17A blockade. However, the nature of the cell populations that produce this important proinflammatory cytokine remains poorly defined. We undertook this study to characterize the major IL-17A-producing blood cell populations in the peripheral blood of patients with axial SpA, with a focus on mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, a population known to be capable of producing IL-17.
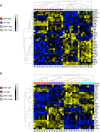
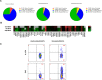
Methods: We evaluated IL-17A production from 5 sorted peripheral blood cell populations, namely, MAIT cells, γδ T cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and neutrophils, before and after stimulation with phorbol myristate acetate, the calcium ionophore A23187, and β-1,3-glucan. Expression of IL-17A transcripts and protein were determined using nCounter and ultra-sensitive Simoa technology, respectively. MAIT cells from the axial entheses of non-axial SpA control patients (n = 5) were further characterized using flow cytometric immunophenotyping and quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and the production of IL-17 was assessed following stimulation.
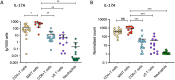
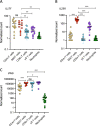
Results: On a per-cell basis, MAIT cells from peripheral blood produced the most IL-17A compared to CD4+ T cells (P < 0.01), CD8+ T cells (P < 0.0001), and γδ T cells (P < 0.0001). IL-17A was not produced by neutrophils. Gene expression analysis also revealed significantly higher expression of IL17A and IL23R in MAIT cells. Stimulation of peripheral blood MAIT cells with anti-CD3/CD28 and IL-7 and/or IL-18 induced strong expression of IL17F. MAIT cells were present in the normal, unaffected entheses of control patients who did not have axial SpA and showed elevated AHR, JAK1, STAT4, and TGFB1 transcript expression with inducible IL-17A protein. IL-18 protein expression was evident in spinal enthesis digests.
Conclusion: Both peripheral blood MAIT cells and resident MAIT cells in normal axial entheses contribute to the production of IL-17 and may play important roles in the pathogenesis of axial SpA.
© 2022 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Characterization of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in blood of patients with axial spondyloarthritis and in axial entheses of healthy controls: comment on the article by Rosine et al.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022 Dec;74(12):2045-2046. doi: 10.1002/art.42278. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35762820 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The paradigm of IL-23-independent production of IL-17F and IL-17A and their role in chronic inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1191782. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1191782. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucosal-associated invariant T cells in patients with axial spondyloarthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 10;14:1128270. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1128270. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969157 Free PMC article.
-
Functional significance of MAIT cells in psoriatic arthritis.Cytokine. 2020 Jan;125:154855. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154855. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31541902
-
Gut Inflammation in Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients is Characterized by a Marked Type 17 Skewed Mucosal Innate-like T Cell Signature.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 Nov;75(11):1969-1982. doi: 10.1002/art.42627. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37293832
-
Whodunit? The Contribution of Interleukin (IL)-17/IL-22-Producing γδ T Cells, αβ T Cells, and Innate Lymphoid Cells to the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 25;9:885. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00885. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29922283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the Underworld of Axial Spondyloarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 30;24(7):6463. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076463. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-23 tunes inflammatory functions of human mucosal-associated invariant T cells.iScience. 2025 Jan 25;28(2):111898. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.111898. eCollection 2025 Feb 21. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40008359 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Spondyloarthritis Pathogenesis: The Promise of Single-Cell Profiling.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024 Apr;26(4):144-154. doi: 10.1007/s11926-023-01132-7. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38227172 Review.
-
The paradigm of IL-23-independent production of IL-17F and IL-17A and their role in chronic inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1191782. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1191782. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Early Treatment in the Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis: Challenges and Opportunities.Rheumatol Ther. 2024 Feb;11(1):19-34. doi: 10.1007/s40744-023-00627-0. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Rheumatol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38108992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baeten D, Baraliakos X, Braun J, et al. Anti‐interleukin‐17A monoclonal antibody secukinumab in treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2013;382:1705–13. - PubMed
-
- Van der Heijde D, Wei JC, Dougados M, et al. Ixekizumab, an interleukin‐17A antagonist in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis or radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in patients previously untreated with biological disease‐modifying anti‐rheumatic drugs (COAST‐V): 16‐week results of a phase 3 randomised, double‐blind, active‐controlled and placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2018;398:2441–51. - PubMed
-
- Jandus C, Bioley G, Rivals JP, et al. Increased numbers of circulating polyfunctional Th17 memory cells in patients with seronegative spondylarthritides. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:2307–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

