Nusinersen efficacy data for 24-month in type 2 and 3 spinal muscular atrophy
- PMID: 35166467
- PMCID: PMC8935309
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51514
Nusinersen efficacy data for 24-month in type 2 and 3 spinal muscular atrophy
Abstract
The study reports real world data in type 2 and 3 SMA patients treated for at least 2 years with nusinersen. Increase in motor function was observed after 12 months and during the second year. The magnitude of change was variable across age and functional subgroup, with the largest changes observed in young patients with higher function at baseline. When compared to natural history data, the difference between study cohort and untreated patients swas significant on both Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale and Revised Upper Limb Module both at 12 months and at 24 months.
© 2022 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
MCP, GC, VAS, SM, ADA, CB, FS, EA, RDS, EB, MP, and EM have been consultant for BIOGEN S.R.L. which owns patent rights to nusinersen that was used in this study.
Figures
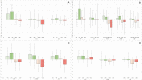
Comment in
-
SMA type 2 and 3 improvements over 2 years.Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Apr;18(4):187. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00640-x. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35228704 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mercuri E, Pera MC, Scoto M, Finkel R, Muntoni F. Spinal muscular atrophy ‐ insights and challenges in the treatment era. Nat Rev Neurol. 2020;16(12):706‐715. - PubMed
-
- Day JW, Finkel RS, Chiriboga CA, et al. Onasemnogene abeparvovec gene therapy for symptomatic infantile‐onset spinal muscular atrophy in patients with two copies of SMN2 (STR1VE): an open‐label, single‐arm, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(4):284‐293. - PubMed
-
- Broekhoff TF, Sweegers CCG, Krijkamp EM, et al. Early cost‐effectiveness of onasemnogene abeparvovec‐xioi (zolgensma) and nusinersen (spinraza) treatment for spinal muscular atrophy i in The Netherlands with relapse scenarios. Value Health. 2021;24(6):759‐769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

