Development of a Metric to Detect and Decrease Low-Value Prescribing in Older Adults
- PMID: 35166780
- PMCID: PMC8848205
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48599
Development of a Metric to Detect and Decrease Low-Value Prescribing in Older Adults
Abstract
Importance: Metrics that detect low-value care in common forms of health care data, such as administrative claims or electronic health records, primarily focus on tests and procedures but not on medications, representing a major gap in the ability to systematically measure low-value prescribing.
Objective: To develop a scalable and broadly applicable metric that contains a set of quality indicators (EVOLV-Rx) for use in health care data to detect and reduce low-value prescribing among older adults and that is informed by diverse stakeholders' perspectives.
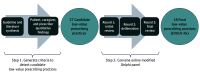
Design, setting, and participants: This qualitative study used an online modified-Delphi method to convene an expert panel of 15 physicians and pharmacists. This panel, comprising clinicians, health system leaders, and researchers, was tasked with rating and discussing candidate low-value prescribing practices that were derived from medication safety criteria; peer-reviewed literature; and qualitative studies of patient, caregiver, and physician perspectives. The RAND ExpertLens online platform was used to conduct the activities of the panel. The panelists were engaged for 3 rounds between January 1 and March 31, 2021.
Main outcomes and measures: Panelists used a 9-point Likert scale to rate and then discuss the scientific validity and clinical usefulness of the criteria to detect low-value prescribing practices. Candidate low-value prescribing practices were rated as follows: 1 to 3, indicating low validity or usefulness; 3.5 to 6, uncertain validity or usefulness; and 6.5 to 9, high validity or usefulness. Agreement among panelists and the degree of scientific validity and clinical usefulness were assessed using the RAND/UCLA (University of California, Los Angeles) Appropriateness Method.
Results: Of the 527 low-value prescribing recommendations identified, 27 discrete candidate low-value prescribing practices were considered for inclusion in EVOLV-Rx. After round 1, 18 candidate practices were rated by the panel as having high scientific validity and clinical usefulness (scores of ≥6.5). After round 2 panel deliberations, the criteria to detect 19 candidate practices were revised. After round 3, 18 candidate practices met the inclusion criteria, receiving final median scores of 6.5 or higher for both scientific validity and clinical usefulness. Of those practices that were not included in the final version of EVOLV-Rx, 3 received high scientific validity (scores ≥6.5) but uncertain clinical usefulness (scores <6.5) ratings, whereas 6 received uncertain scientific validity rating (scores <6.5).
Conclusions and relevance: This study culminated in the development of EVOLV-Rx and involved a panel of experts who identified the 18 most salient low-value prescribing practices in the care of older adults. Applying EVOLV-Rx may enhance the detection of low-value prescribing practices, reduce polypharmacy, and enable older adults to receive high-value care across the full spectrum of health services.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Considering Value in Prescribing and Deprescribing for Older Adults.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Feb 1;5(2):e2148606. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48606. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35166789 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous