The role of ferroptosis in acute lung injury
- PMID: 35166985
- PMCID: PMC8853161
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-021-04327-7
The role of ferroptosis in acute lung injury
Abstract
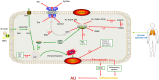
Acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI/ARDS) is a common disease with high morbidity and mortality, and its pathogenesis is believed to be related to oxidative stress, apoptosis, inflammation, and hypoxia. Ferroptosis is a type of nonapoptotic cell death characterized by iron-dependent lipid peroxide accumulation and is involved in many cellular physiological processes. Recent studies have confirmed that ferroptosis may be involved in the development of ALI. This review summarizes the most recent discoveries on the role of ferroptosis in ALI to provide new strategies for its prevention and treatment.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Ferroptosis; Glutathione peroxidase 4; Lipid peroxidation.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kalil AC, Patterson TF, Mehta AK, Tomashek KM, Wolfe CR, Ghazaryan V, Marconi VC, Ruiz-Palacios GM, Hsieh L, Kline S, Tapson V, Iovine NM, Jain MK, Sweeney DA, El Sahly HM, Branche AR, Regalado Pineda J, Lye DC, Sandkovsky U, Luetkemeyer AF, Cohen SH, Finberg RW, Jackson PEH, Taiwo B, Paules CI, Arguinchona H, Erdmann N, Ahuja N, Frank M, Oh MD, Kim ES, Tan SY, Mularski RA, Nielsen H, Ponce PO, Taylor BS, Larson L, Rouphael NG, Saklawi Y, Cantos VD, Ko ER, Engemann JJ, Amin AN, Watanabe M, Billings J, Elie MC, Davey RT, Burgess TH, Ferreira J, Green M, Makowski M, Cardoso A, de Bono S, Bonnett T, Proschan M, Deye GA, Dempsey W, Nayak SU, Dodd LE, Beigel JH. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):795–807. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031994. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

