Dysregulated circulating miR-4429 serves as a novel non-invasive biomarker and is correlated with EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35167433
- PMCID: PMC9392976
- DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2021.6450
Dysregulated circulating miR-4429 serves as a novel non-invasive biomarker and is correlated with EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
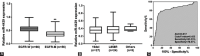
This study aimed to investigate the correlation between microRNA (miR)-4429 and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), the expression and clinical significance of miR-4429 in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and the relationship between miR-4429 and EGFR mutation in NSCLC patients. Blood samples were collected from 122 NSCLC patients and 72 healthy volunteers. miR-4429 expression and EGFR mRNA expression were detected by real-time quantitative PCR. Correlation between miR-4429 and EGFR was evaluated by dual‑luciferase reporter assay and the Pearson correlation analysis. The ability of serum miR‑4429 to discriminate between NSCLC patients and healthy controls, and to discriminate between EGFR wild-type (EGFR-W) and EGFR mutant-type (EGFR-M) patients was assessed using receiver operating characteristic analysis. The relationship between miR-4429 and NSCLC patients' survival was identified by Kaplan-Meier survival curves and log-rank test. The prognostic value of miR-4429 in NSCLC patients was evaluated by Cox regression analysis. miR-4429 could directly bind to EGFR. Serum miR-4429, decreased in NSCLC patients, was negatively correlated with serum EGFR mRNA expression in NSCLC patients. Additionally, miR-4429 had a high diagnostic value for screening NSCLC patients from healthy controls, and was independently correlated with survival prognosis of NSCLC patients. Moreover, miR‑4429 was decreased in EGFR-M patients, which had a certain screening ability for EGFR‑M patients. Our findings indicate that miR-4429 is negatively correlated with EGFR in NSCLC, and may function as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for NSCLC patients. Additionally, miR-4429 is associated with EGFR mutation in NSCLC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Amiri A, Pourhanifeh MH, Mirzaei HR, Nahand JS, Moghoofei M, Sahebnasagh R, et al. Exosomes and lung cancer:Roles in pathophysiology, diagnosis and therapeutic applications. Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(2):308–28. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867327666200204141952. - PubMed
-
- Inamura K. Lung cancer:Understanding its molecular pathology and the 2015 WHO classification. Front Oncol. 2017;7:193. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2017.00193. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Su Z, Chen M, Ding R, Shui L, Zhao Q, Luo W. Long noncoding RNA HCG11 suppresses the malignant phenotype of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by targeting a miR875/SATB2 axis. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(2):552. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.12191. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Salehi M, Movahedpour A, Tayarani A, Shabaninejad Z, Pourhanifeh MH, Mortezapour E, et al. Therapeutic potentials of curcumin in the treatment of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Phytother Res. 2020;34(10):2557–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6704. - PubMed
-
- Rezaei S, Mahjoubin-Tehran M, Aghaee-Bakhtiari SH, Jalili A, Movahedpour A, Khan H, et al. Autophagy-related MicroRNAs in chronic lung diseases and lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020;153:103063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.103063. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

