Intraocular pressure after myopic laser refractive surgery measured with a new Goldmann convex prism: correlations with GAT and ORA
- PMID: 35168601
- PMCID: PMC8849021
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-022-02309-x
Intraocular pressure after myopic laser refractive surgery measured with a new Goldmann convex prism: correlations with GAT and ORA
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study is to describe measurements using a newly developed modified Goldmann convex tonometer (CT) 1 year after myopic laser refractive surgery. Intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements were compared with IOP values obtained by Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT), and Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA).
Methods: Prospective double-masked study performed on thirty eyes of thirty patients that underwent laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK; n = 19) or photorefractive keratectomy (PRK; n = 11). IOP was measured before and 3 and 12 months after surgery. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland-Altman plot were calculated to assess the agreement between GAT, CT, IOPg (Goldmann-correlated IOP) and IOPcc (corneal-compensated IOP) from ORA.
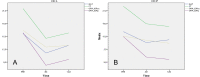
Results: Twelve months after LASIK, IOP measured with CT showed the best correlation with IOP measured with GAT before surgery (GATpre) (ICC = 0.886, 95% CI: 0.703-0.956) (15.60 ± 3.27 vs 15.80 ± 3.22; p < 0.000). However, a moderate correlation was found for IOP measured with IOPcc and CT 12 months after LASIK (ICC = 0.568, 95% CI: - 0.185 - 0.843) (15.80 ± 3.22 vs 12.87 ± 2.77; p < 0.004). Twelve months after PRK, CT showed a weak correlation (ICC = - 0.266, 95% CI: - 3.896 - 0.663), compared to GATpre (17.30 ± 3.47 vs 16.01 ± 1.45; p < 0.642), as well as poor correlation (ICC = 0.256, 95% CI: - 0.332 - 0.719) with IOPcc (17.30 ± 3.47 vs 13.38 ± 1.65; p < 0.182).
Conclusions: Twelve months after LASIK, IOP measured with CT strongly correlated with GAT before surgery and could therefore provide an alternative method for measuring IOP after this surgery. More studies regarding this new convex prism are needed to assess its accuracy.
Keywords: Corneal biomechanics; Glaucoma; Intraocular pressure; LASIK; Myopia; PRK; Tonometry.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Each of the co-authors has seen and agrees with the financial and non-financial competing interests statement presented by MI (as corresponding author) on behalf of all the authors of the paper:
MI has personal conflict of interest being the inventor of the new Goldmann “CT” applanation tonometer. She had full access to all the data in this study and takes complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. MI has exclusive personal rights to the intellectual property of this invention secured by the patents referred to above, and is the owner of every figure presented in this study.
The rest of the co-authors declare no financial competing interests.
MI and the rest of the co-authors declare they do not have non-financial competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Goldmann and modified Goldmann tonometry measuring intraocular pressure changes in eyes which underwent myopic laser in situ Keratomileusis and photorefractive keratectomy.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Dec 20;22(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02741-z. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36539706 Free PMC article.
-
Intraocular Pressure Changes in Myopic Patients Undergoing Laser <em>In-Situ Keratomileusis</em> and Photorefractive Keratectomy.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2023 Oct;33(10):1148-1152. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2023.10.1148. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2023. PMID: 37804021
-
Effectiveness of the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer, the Dynamic Contour Tonometer, the Ocular Response Analyzer and the Corvis ST in Measuring Intraocular Pressure following FS-LASIK.Curr Eye Res. 2020 Feb;45(2):144-152. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2019.1660794. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Curr Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31869261
-
Comparison of intraocular pressure measured by ocular response analyzer and Goldmann applanation tonometer after corneal refractive surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Jan 10;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1288-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31924174 Free PMC article.
-
PHOTOREFRACTIVE SURGERY WITH EXCIMER LASER AND ITS IMPACT ON THE DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW-UP OF GLAUCOMA. A REVIEW.Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2021 Winter;77(6):276-283. doi: 10.31348/2021/8. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2021. PMID: 35081716 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Goldmann and modified Goldmann tonometry measuring intraocular pressure changes in eyes which underwent myopic laser in situ Keratomileusis and photorefractive keratectomy.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Dec 20;22(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02741-z. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36539706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shin J, Kim TW, Park SJ, Yoon M, Lee JW. Changes in biomechanical properties of the cornea and intraocular pressure after myopic laser in situ keratomileusis using a femtosecond laser for flap creation determined using ocular response analyzer and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Glaucoma. 2015;24(3):195–201. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e31829da1ec. - DOI - PubMed

