Combination stem cell therapy using dental pulp stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells for critical hindlimb ischemia
- PMID: 35168701
- PMCID: PMC9340082
- DOI: 10.5483/BMBRep.2022.55.7.003
Combination stem cell therapy using dental pulp stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells for critical hindlimb ischemia
Abstract
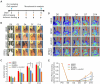
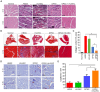
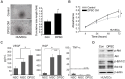
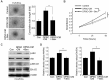
Narrowing of arteries supplying blood to the limbs provokes critical hindlimb ischemia (CLI). Although CLI results in irreversible sequelae, such as amputation, few therapeutic options induce the formation of new functional blood vessels. Based on the proangiogenic potentials of stem cells, in this study, it was examined whether a combination of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) could result in enhanced therapeutic effects of stem cells for CLI compared with those of DPSCs or HUVECs alone. The DPSCs+ HUVECs combination therapy resulted in significantly higher blood flow and lower ischemia damage than DPSCs or HUVECs alone. The improved therapeutic effects in the DPSCs+ HUVECs group were accompanied by a significantly higher number of microvessels in the ischemic tissue than in the other groups. In vitro proliferation and tube formation assay showed that VEGF in the conditioned media of DPSCs induced proliferation and vessel-like tube formation of HUVECs. Altogether, our results demonstrated that the combination of DPSCs and HUVECs had significantly better therapeutic effects on CLI via VEGF-mediated crosstalk. This combinational strategy could be used to develop novel clinical protocols for CLI proangiogenic regenerative treatments. [BMB Reports 2022; 55(7): 336-341].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dental pulp stem cells overexpressing stromal-derived factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor in dental pulp regeneration.Clin Oral Investig. 2019 May;23(5):2497-2509. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2699-0. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Clin Oral Investig. 2019. PMID: 30315421
-
Activin a regulates vascular formation and stabilization in direct coculture of dental pulp stem cells and endothelial cells.Int Endod J. 2025 Jul;58(7):991-1005. doi: 10.1111/iej.14226. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Int Endod J. 2025. PMID: 40106315 Free PMC article.
-
DPSCs treated by TGF-β1 regulate angiogenic sprouting of three-dimensionally co-cultured HUVECs and DPSCs through VEGF-Ang-Tie2 signaling.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 May 10;12(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02349-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33971955 Free PMC article.
-
EphrinB2/EphB4 Signaling Regulates DPSCs to Induce Sprouting Angiogenesis of Endothelial Cells.J Dent Res. 2019 Jul;98(7):803-812. doi: 10.1177/0022034519843886. Epub 2019 Apr 24. J Dent Res. 2019. PMID: 31017515
-
The use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor induced mobilization for isolation of dental pulp stem cells with high regenerative potential.Biomaterials. 2013 Dec;34(36):9036-47. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23988014
Cited by
-
PA2G4/EBP1 ubiquitination by PRKN/PARKIN promotes mitophagy protecting neuron death in cerebral ischemia.Autophagy. 2024 Feb;20(2):365-379. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2259215. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 37712850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johannesson A, Larsson GU, Ramstrand N, Turkiewicz A, Wirehn AB, Atroshi I. Incidence of lower-limb amputation in the diabetic and nondiabetic general population: a 10-year population-based cohort study of initial unilateral and contralateral amputations and reamputations. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:275–280. doi: 10.2337/dc08-1639. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

