Communicate hope to motivate the public during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 35169174
- PMCID: PMC8847429
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-06316-2
Communicate hope to motivate the public during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
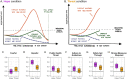
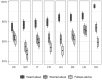
How should health authorities communicate to motivate the public to comply with health advice during a prolonged health crisis such as a pandemic? During the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, for example, people have had to comply with successive restrictions as the world faced multiple races between controlling new waves of the virus and the development and implementation of vaccines. Here, we examine how health authorities and governments most effectively motivate the public by focusing on a specific race: between the Alpha variant and the implementation of the first generation of COVID-19 vaccinations in the winter of 2021. Following prior research on crisis communication, we focus on appeals to fear and hope using communicative aids in the form of visualizations based on epidemiological modelling. Using a population-based experiment conducted in United States ([Formula: see text]), we demonstrate that a hope-oriented visual communication aid, depicting the competing effects on the epidemic curve of (1) a more infectious variant and (2) vaccinations, motivates public action more effectively than a fear-oriented visual communication, focusing exclusively on the threat of the new variant. The importance of the implementation of such hope-oriented messages is further highlighted by cross-national representative surveys from eight countries ([Formula: see text]), which demonstrate that feelings of fear towards the Alpha variant alone were insufficient to activate strong compliance. Overall, these findings provide general insights into the importance of hope as a health communication strategy during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Amidon TR, Nielsen AC, Pflugfelder EH, Richards DP, Stephens SH. Visual risk literacy in “flatten the curve” covid-19 visualizations. J. Bus. Tech. Commun. 2021;35(1):101–109. doi: 10.1177/1050651920963439. - DOI
-
- Chaiuk TA, Dunaievska OV. Fear culture in media: An examination on coronavirus discourse. J. History Cult. Art Res. 2020;9(2):184–194. doi: 10.7596/taksad.v9i2.2636. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

