Lipidome profile predictive of disease evolution and activity in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 35169224
- PMCID: PMC8894401
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-022-00725-z
Lipidome profile predictive of disease evolution and activity in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
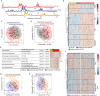
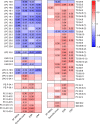
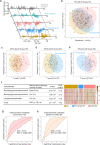
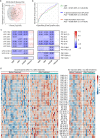
Lipid mediators are crucial for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA); however, global analyses have not been undertaken to systematically define the lipidome underlying the dynamics of disease evolution, activation, and resolution. Here, we performed untargeted lipidomics analysis of synovial fluid and serum from RA patients at different disease activities and clinical phases (preclinical phase to active phase to sustained remission). We found that the lipidome profile in RA joint fluid was severely perturbed and that this correlated with the extent of inflammation and severity of synovitis on ultrasonography. The serum lipidome profile of active RA, albeit less prominent than the synovial lipidome, was also distinguishable from that of RA in the sustained remission phase and from that of noninflammatory osteoarthritis. Of note, the serum lipidome profile at the preclinical phase of RA closely mimicked that of active RA. Specifically, alterations in a set of lysophosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylcholine, ether-linked phosphatidylethanolamine, and sphingomyelin subclasses correlated with RA activity, reflecting treatment responses to anti-rheumatic drugs when monitored serially. Collectively, these results suggest that analysis of lipidome profiles is useful for identifying biomarker candidates that predict the evolution of preclinical to definitive RA and could facilitate the assessment of disease activity and treatment outcomes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Smolen JS, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020;79:685–699. - PubMed
-
- Ajeganova S, et al. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-free sustained remission in rheumatoid arthritis: an increasingly achievable outcome with subsidence of disease symptoms. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016;75:867–873. - PubMed
-
- Mankia K, Emery P. Preclinical rheumatoid arthritis: Progress toward prevention. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:779–788. - PubMed
-
- Nielen MMJ, et al. Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: A study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:380–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

