Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs
- PMID: 35169296
- PMCID: PMC8901656
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-022-00948-7
Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs
Abstract
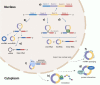
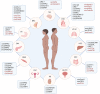
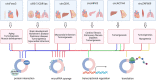
In recent years, circular RNAs (circRNAs), a new class of RNA molecules characterized by their covalently closed circular structure, have become a new research paradigm in RNA biology. Many circRNAs are conserved among eukaryotes, localize in specific subcellular compartments, and play different biological roles. Accumulating evidence shows that circRNAs regulate a diversity of cellular processes by acting as miRNA sponges, anchors for circRNA binding proteins (cRBPs), transcriptional regulators, molecular scaffolds, and sources for translation of small proteins/peptides. The emergence of the biological functions of circRNAs has brought a new perspective to our understanding of cellular physiology and disease pathogenesis. Recent studies have shown that the expression of circRNAs is tissue- and cell type-specific and specifically regulated through development or disease progression, where they exert specific biological functions. However, the mechanisms underlying these remain largely unknown. A deeper understanding of how the specific expression of circRNAs is regulated to exert specific biological functions will enable the use of circRNA as a biomarker in clinical practice and the development of new therapeutic approaches. This review aims to summarize recent developments in circRNA biogenesis, functions, and molecular mechanisms. We also provide some specific circRNAs as examples to show their tissue-specific distribution and evaluate the possibility of applying circRNA technologies in molecular research and therapeutics.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to ADMC Associazione Differenziamento e Morte Cellulare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circular RNA in Pancreatic Cancer: Biogenesis, Mechanism, Function and Clinical Application.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Feb 28;22(7):1612-1629. doi: 10.7150/ijms.107773. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40093798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircRNA: a rising star in plant biology.J Genet Genomics. 2022 Dec;49(12):1081-1092. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2022.05.004. Epub 2022 May 27. J Genet Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35644325 Review.
-
Circular RNA-protein interactions: functions, mechanisms, and identification.Theranostics. 2020 Feb 10;10(8):3503-3517. doi: 10.7150/thno.42174. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32206104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translation and functional roles of circular RNAs in human cancer.Mol Cancer. 2020 Feb 15;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1135-7. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32059672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification, biogenesis, function, and mechanism of action of circular RNAs in plants.Plant Commun. 2023 Jan 9;4(1):100430. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2022.100430. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Plant Commun. 2023. PMID: 36081344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
circPTP4A2 knockdown suppresses NSCLC progression via regulating proliferation and activating anti-tumor immunity.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Jul 16;19(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-02964-9. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 39014449 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa_circ_0022383 promote non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis through regulating the miR-495-3p/KPNA2 axis.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 19;23(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03068-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37981709 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA in cervical cancer: Fundamental mechanism and clinical potential.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Nov 18;9(1):116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.11.009. eCollection 2024 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 38035041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel protein encoded by circVPS13D attenuates antiviral innate immunity by targeting MAVS in teleost fish.J Virol. 2023 Nov 30;97(11):e0088623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00886-23. Epub 2023 Oct 16. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37843373 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA-encoded oncogenic PIAS1 variant blocks immunogenic ferroptosis by modulating the balance between SUMOylation and phosphorylation of STAT1.Mol Cancer. 2024 Sep 28;23(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02124-6. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39334380 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

