Novel truncating variant in KMT2E associated with cerebellar hypoplasia and velopharyngeal dysfunction
- PMID: 35169466
- PMCID: PMC8832165
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.5277
Novel truncating variant in KMT2E associated with cerebellar hypoplasia and velopharyngeal dysfunction
Abstract
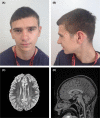
KMT2E-related neurodevelopmental disorder is a recently described intellectual disability syndrome often with speech difficulties. Here, we describe an individual with a heterozygous frameshift variant in KMT2E (NM_182931.2:c.2334_2337delTTAC, p.[Tyr779AlafsTer41]), intellectual disability, cerebellar hypoplasia, and velopharyngeal dysfunction. This case suggests potential mechanisms of speech disturbance in the disorder, requiring further investigation.
Keywords: KMT2E; cerebellar hypoplasia; neurodevelopmental disorder; velopharyngeal dysfunction.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has a relevant conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American college of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17(5):405‐424. doi:10.1038/gim.2015.30 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

