Five Year Trends in the Utilization of Robotic Bariatric Surgery Procedures, United States 2015-2019
- PMID: 35169953
- PMCID: PMC12292007
- DOI: 10.1007/s11695-022-05964-7
Five Year Trends in the Utilization of Robotic Bariatric Surgery Procedures, United States 2015-2019
Abstract
Purpose: Robotic approaches have been steadily replacing laparoscopic approaches in metabolic and bariatric surgeries (MBS); however, their superiority has not been rigorously evaluated. The main goal of the study was to evaluate the 5-year utilization trends of robotic MBS and to compare to laparoscopic outcomes.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of 2015-2019 MBSAQIP data. Kruskal-Wallis test/Wilcoxon and Fisher's exact/chi-square were used to compare continuous and categorical variables, respectively. Generalized linear models were used to compare surgery outcomes.
Results: The use of robotic MBS increased from 6.2% in 2015 to 13.5% in 2019 (N= 775,258). Robotic MBS patients had significantly higher age, BMI, and likelihood of 12 diseases compared to laparoscopic patients. After adjustment, robotic MBS patients showed higher 30-day interventions and 30-day readmissions alongside longer surgery time (26-38 min).
Conclusion: Robotic MBS shows higher intervention and readmission even after controlling for cofounding variables.
Keywords: Laparoscopic bariatric surgery; MBS; Robotic bariatric surgery.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
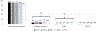
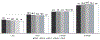
References
-
- Pernar LIM, Robertson FC, Tavakkoli A, et al. An appraisal of the learning curve in robotic general surgery. Surg Endosc 2017;31(11):4583–96 - PubMed
-
- Tatarian T, Yang J, Wang J, et al. Trends in the utilization and perioperative outcomes of primary robotic bariatric surgery from 2015 to 2018: a study of 46,764 patients from the MBSAQIP data registry. Surg Endosc 2021;35(7):3915–22 - PubMed
-
- Scarritt T, Hsu CH, Maegawa FB, et al. Trends in utilization and perioperative outcomes in robotic-assisted bariatric surgery using the MBSAQIP database: A 4-Year Analysis. Obes Surg 2021;31(2):854–61 - PubMed
-
- Li K, Zou J, Tang J, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg 2016;26(12):3031–44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

